Category filter
Reducing Exposure: Mastering Risk-Based Vulnerability Management at Scale
Document Overview
In a massive enterprise estate, traditional periodic vulnerability scans (polling intervals of 4–24 hours) leave critical exposure windows. Hexnode Vulnerability Management shifts the paradigm from reactive scanning to Real-Time Risk Orchestration.
By utilizing a resident agent architecture, Hexnode correlates live device inventory—OS versions, installed binaries, and registry configurations—directly with the Global Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) database. This empowers the 500-technician operational team to instantly identify risk and orchestrate remediation across 500,000 endpoints without WAN saturation.
The CVE Correlation Engine
The core of this capability is the Real-Time Telemetry Architecture, which ensures vulnerability data is actionable within seconds, not days.
1. Live Inventory Mapping (The “Triple-Channel” Feed)
Hexnode maintains a continuous state of awareness using three distinct communication protocols to ensure 99.9% uptime and data accuracy:
- Persistent WebSockets: Maintains an “always-on” connection for instant command execution.
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport): Lightweight protocol for streaming granular device attributes (build numbers, app versions) with minimal bandwidth overhead.
- Native Push Services (APNs/FCM/WNS): Wakes sleeping devices to force critical check-ins.
2. Dynamic Risk Scoring
- Automated Cross-Referencing: The engine automatically maps the live software inventory against the NIST National Vulnerability Database (NVD).
- CVSS Contextualization: Devices are not just flagged as “vulnerable”; they are assigned a Vulnerability Score based on the CVSS v3.1 (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) severity of active CVEs. This allows technicians to prioritize a “Critical” (9.0+) vulnerability over a “Low” (3.0) risk during triage.
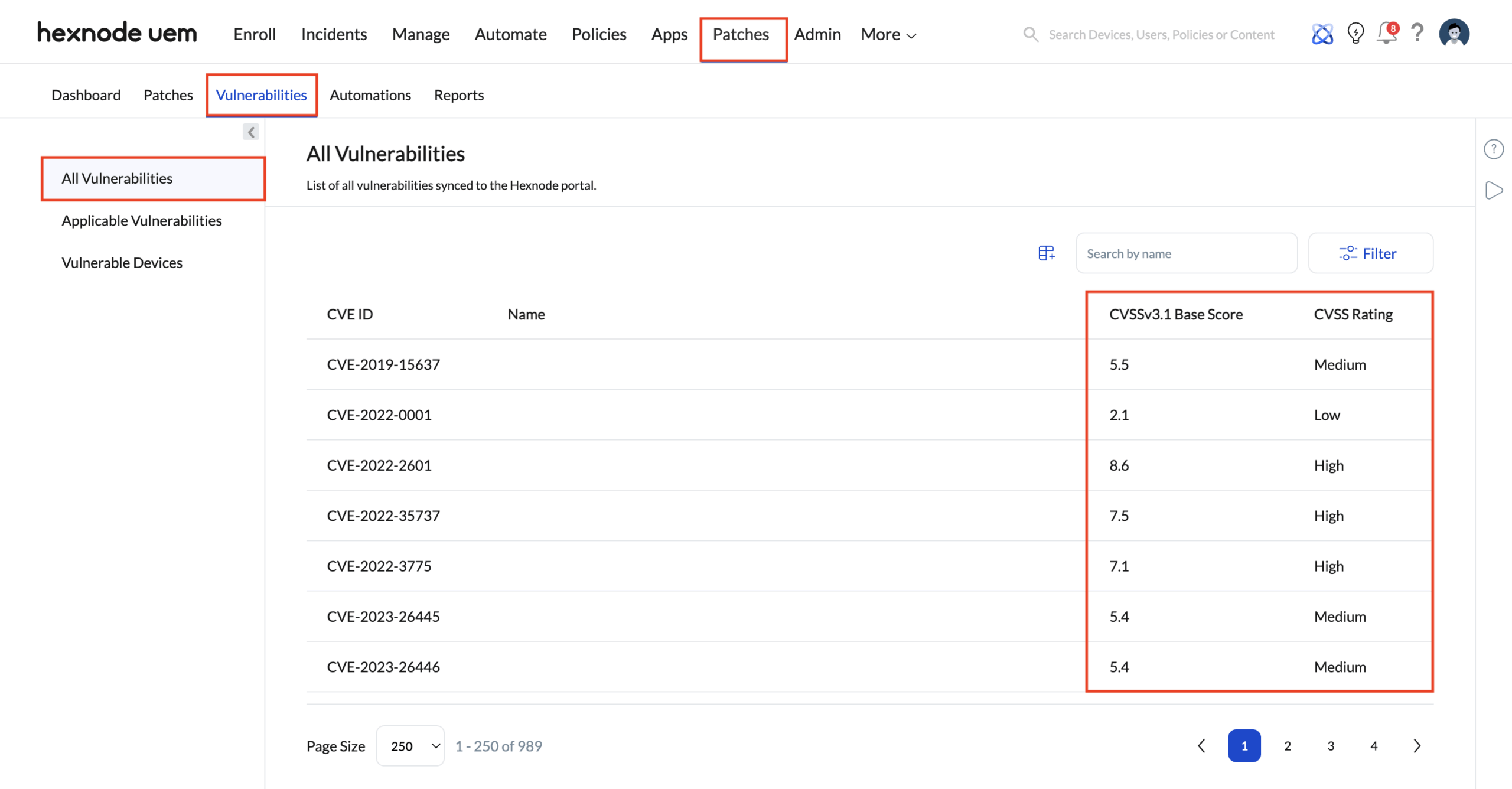
3. Zero-Day Visibility (Search-to-Insight)
When a zero-day threat (e.g., Log4j or PrintNightmare) is disclosed:
- No Rescan Required: Technicians query the CVE Dashboard using the CVE-ID (e.g., CVE-2021-44228).
- Instant Impact Analysis: Because inventory data is streamed via MQTT, the dashboard instantly populates the exact count of 500k devices hosting the vulnerable binary, bypassing the need for a fleet-wide manual scan.
Mass Remediation Workflows
Identification is the trigger; remediation is the outcome. Hexnode leverages DAFS and Genie AI to close the vulnerability gap at an enterprise scale.
1. One-Click Patching via DAFS
Deploying 500MB patch to 500,000 devices simultaneously would cripple the corporate WAN. Hexnode solves this with DAFS (Distributed Apps and Files Server).
- Local Caching: A designated device (Windows/macOS) in each regional branch acts as a local DAFS node.
- WAN Optimization: The patch is downloaded once from the Hexnode Cloud to the DAFS node. All other devices in that subnet pull the patch locally via LAN/P2P, reducing internet bandwidth consumption by up to 90%.
2. Agentic Remediation (Hexnode Genie AI)
For vulnerabilities that cannot be fixed by a standard OS patch (e.g., requiring a registry tweak, service disablement, or port closure):
- AI-Generated Scripts: Technicians utilize Hexnode Genie, an NLP-powered coding assistant, to generate remediation scripts (PowerShell for Windows, Bash for macOS/Linux) by simply typing: “Disable Print Spooler service and delete registry key X.”
- Sub-Second Execution: Validated scripts are executed via the Execute Custom Script action. The WebSocket connection ensures the script runs immediately, returning exit codes (Success/Fail) to the dashboard in real-time.
Enterprise Vulnerability Reporting
To manage governance across 50 sub-companies, visibility is tiered by role:
| Metric Level | Target Audience | Insight Provided |
|---|---|---|
| Global Risk Heatmap | CISO / Execs | Aggregated compliance status (Red/Amber/Green) across the entire 500k estate. |
| SLA Tracking | Regional Managers | “Mean Time to Remediate” (MTTR) tracking against the 48-hour critical patch SLA. |
| CVE Detail View | Security Ops | Granular list of Hostname, IP, User, and Patch Status for specific CVEs. |
| Compliance Drift | Automation Engine | Identifies devices that were patched but later manually reverted by users (drift detection). |
Governance & Safety Rails
Executing changes on half a million devices requires strict safety protocols to prevent catastrophic outages.
- Pilot Testing (Canary Deployment): Policies are configured to target a “Pilot Group” (e.g., 1% of the fleet) first. Success criteria (device stability, app functionality) must be met before the update propagates to the “Production” group.
- Auto-Rollback Logic: Using custom scripts and monitoring, if an agent detects boot failures or critical service crashes post-remediation, it can trigger a pre-configured rollback script.
- Immutable Audit Trail: All actions—from script generation by Genie to the final DAFS patch download—are logged in the Action History with timestamps, technician IDs, and outcome statuses for compliance auditing.
Implementation Checklist: Security Phase
- [ ] Action: Configure Automated Compliance Policies to flag devices with CVSS > 8.0 as “Non-Compliant” (quarantining them from corporate email/Wi-Fi).
- [ ] Action: Deploy and authorize DAFS Nodes in all major regional subnets (ensure port 80/443 internal traffic is open).
- [ ] Action: Train L2/L3 technicians on using Hexnode Genie for rapid script generation during zero-day events.