Category filter
How to configure WSUS Specific Settings for Windows devices?
Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) is a tool developed by Microsoft for IT administrators to oversee the distribution of updates released from Microsoft to Windows devices on a network. Configure WSUS specific settings on Windows to enable control over the distribution of Microsoft updates to devices on a network. The primary purpose of WSUS is to guarantee that all Windows devices are up to date, with security patches, thus ensuring the stability of the production environment. The WSUS server presents a wide-range of features that help manage/distribute Windows Updates through a management console. With Hexnode UEM, the IT admin can configure WSUS settings for the Windows devices to centralize the update management process.
Configure WSUS Specific Settings on Window devices with Hexnode UEM
- Login to your Hexnode UEM portal.
- Navigate to the Policies tab.
- Click on New Policy to create a new one or click on any policy to edit an existing one. Enter the Policy Name and Description in the provided fields.
- Navigate to Windows and select WSUS Specific Settings under Patches & Updates.
- Click on Configure.
Update Service URL
Specify the URL of the WSUS server to receive updates from it.
Add alternate Update service URL
Check this option to add an alternate service URL on the network as an internal update service. The Automatic Update client will download the files from the alternate download server if the provided intranet update server lacks the necessary download URLs for the update files.
Alternate Update Service URL
Specify the URL for alternate update service.
Update detection frequency
This setting schedules update checks on Windows within the specified time. Windows adds a random time variance of 0 to 4 hours to the specified time limit. For example, if the update detection is set for every 16 hours, the check for available updates might occur between 16 to 20 hours. If not configured, Windows will check for the updates at the default interval time of 22 hours.
Third-party signed updates
If set to Allowed, it configures Automatic Updates to accept updates signed by entities other than Microsoft, when the update is found on an intranet Microsoft update service location. The updates will be accepted only if they’re signed by a certificate found in the “Trusted Publishers” certificate store of the local computer.
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Allowed | This option is selected by default to allow updates signed by entities other than Microsoft. |
| Not Allowed | This setting prevents Automatic Updates from accepting updates signed by entities other than Microsoft. |
| Not Configured | If the option is set as Not Configured, it will only allow the updates signed by Microsoft. |
Allow online Microsoft Update services
Determine whether the device should be allowed to use Microsoft Update, Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), or Microsoft Store. Enabling this option can cause disruptions in connection to public services such as the Microsoft Store.
Fill empty content URLs
Check this option to allow the Windows Update Agent to automatically determine the download URLs from the alternate source when the files are missing from the update metadata.
Dual Scan
Configure whether the Windows Update client is permitted to initiate automatic scans against Windows Updates when update deferral policies are enabled.
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Allow scan against Windows Update | Select this option to allow the Windows Update client to initiate a scan directly against the Windows Update. |
| Don’t allow update deferral policies to cause scans against Windows Update | Select this option to prevent update deferral policies from automatically initiating scans against Windows Update. |
Proxy behavior for update detection
By default, HTTP WSUS servers require system proxy configuration for scanning. If the system proxy fails, it utilizes the user proxy as a fallback for detecting updates.
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Allow system proxy only for HTTP scans | Selecting this option will allow the use of a system proxy for HTTP scans. |
| Allow user proxy to be used as a fallback if detection using system proxy fails | Selecting this option enables the user proxy to serve as a backup in case the system proxy detection fails. |
Do not enforce Enterprise TLS certificate pinning
Enabling certificate pinning adds a layer of security to the devices by not allowing scans if cert-pinning fails. You can add the certificates to the new WSUS certificate store to enable cert-pinning. The devices will then automatically begin enforcing cert-pinning when scanning the WSUS server. Check this option if you do not want to enforce enterprise TLS certificate pinning when scanning the WSUS server for updates.
Configure update sources
Tick this option to choose whether to receive Windows Updates from the Windows Update endpoint, managed by Windows Update for Business policies, or from the configured Windows Server Update Service (WSUS) server.
The following options will be enabled if “Configure update sources” or “Add alternate Update service URL” is checked.
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Driver Updates | Driver updates refer to the process of updating or replacing the existing software that controls a particular hardware component in a device. |
| Quality Updates | Quality Updates are security updates, incorporating fixes that patch security vulnerabilities and enhance the overall stability of the operating system. |
| Feature Updates | Feature Updates include new features, visual enhancements, and new versions of the operating system. |
| Other Updates | Other Updates in a particular category can consist of updates based on the software or system. It may involve updates, for applications firmware updates, hardware devices, or any other miscellaneous updates that are not classified as driver, quality, or feature updates. |
For the above settings, there are two options to choose from, either Use Windows Updates to receive updates from the Windows Update endpoint, managed by Windows Update for Business policies, or Use WSUS to receive updates from the configured WSUS server.
Apply the WSUS Specific Settings policy with target Windows devices
There are two ways to associate the policy with the devices in bulk.
If the policy hasn’t saved yet,
- Navigate to Policy Targets.
- Click on + Add Devices, search and select the required device(s) to which you need to apply the policy. Click OK.
- Click on Save to apply the policies to the devices.
If the policy has been saved,
- From Policies, choose the policy.
- Click on the Manage drop-down, select Associate Targets and choose the target devices.
- Click Associate.
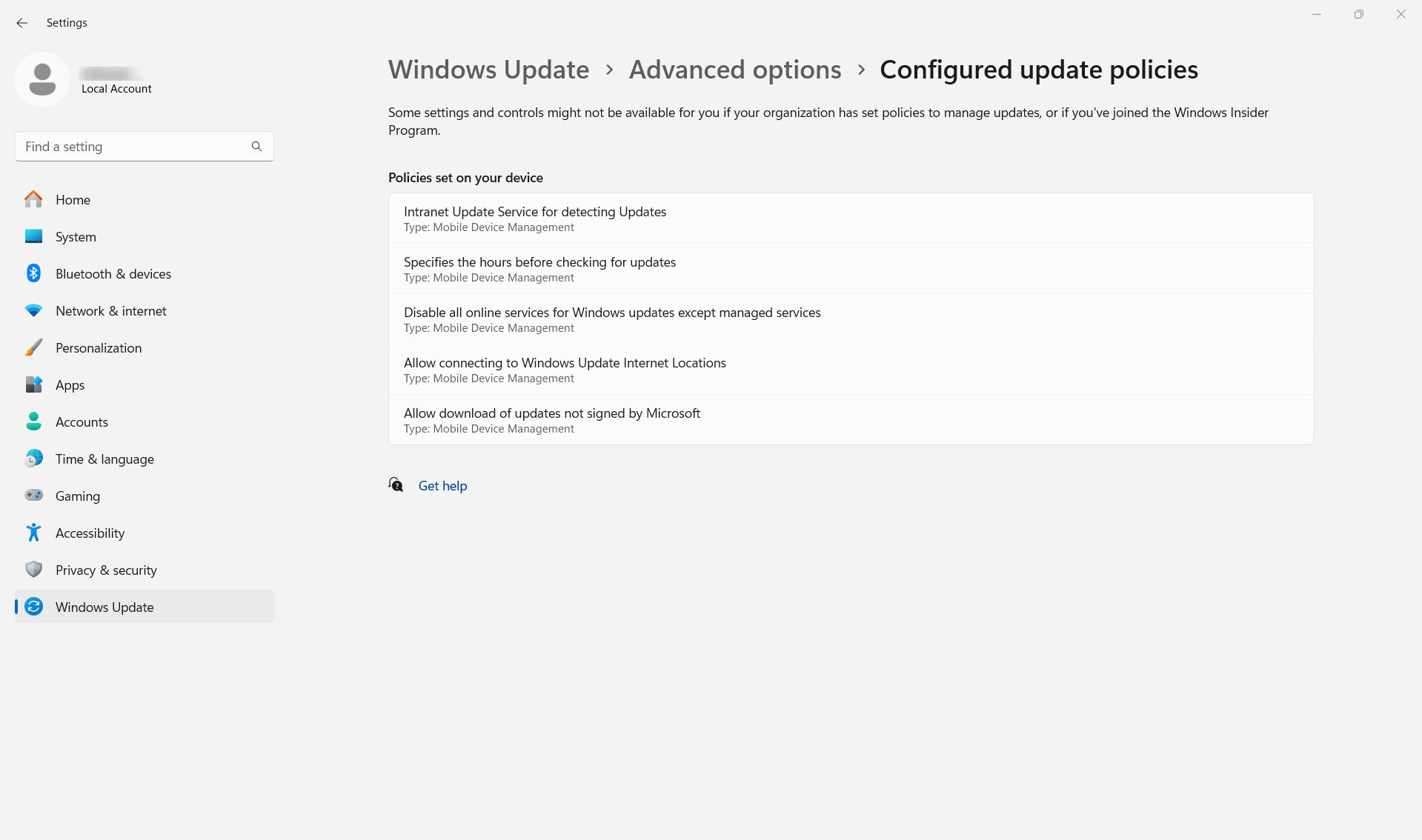
What happens at the device end?
Once the policy is associated, admins can check the configured WSUS specific settings on the Windows device by navigating to Settings > Windows Update > Advanced options > Configured update policies.