Category filter
Event-Driven Automation in Hexnode: Responding to Device and User Events in Real Time
This guide outlines how Hexnode UEM utilizes an Event-Driven Architecture (EDA) paradigm—specifically through Activity Triggers —to automate complex endpoint management tasks. This approach allows the UEM to transition from scheduled, time-based management to a dynamic, real-time, autonomous management solution that reacts instantly to changes in device status, user behavior, and compliance posture.
The Event-Driven Model and Autonomous UEM
In an Event-Driven Architecture, the system reacts to events (a significant change in state) rather than waiting for a scheduled scan or manual instruction. This shift is critical for achieving Autonomous Endpoint Management, where the UEM self-corrects and enforces security instantly.
Event-Driven Workflow
- Event Producer: The managed device (or integrated directory) generates an event (e.g., “Passcode status changed to disabled”).
- Event Broker (Hexnode): The Hexnode UEM Cloud Server receives the event and matches it to a predefined Activity Trigger in the Automate module.
- Event Consumer (Automated Action): The associated workflow is immediately executed on the target device or group.
This asynchronous, real-time response capability ensures policies are applied when they matter most, eliminating security gaps inherent in batch-processing or manual management.
Hexnode UEM Activity Triggers: Enterprise Use Cases
Hexnode’s Automate module allows IT administrators to define complex, multi-action workflows linked directly to specific device events. This is where the true enterprise value of EDA is realized.
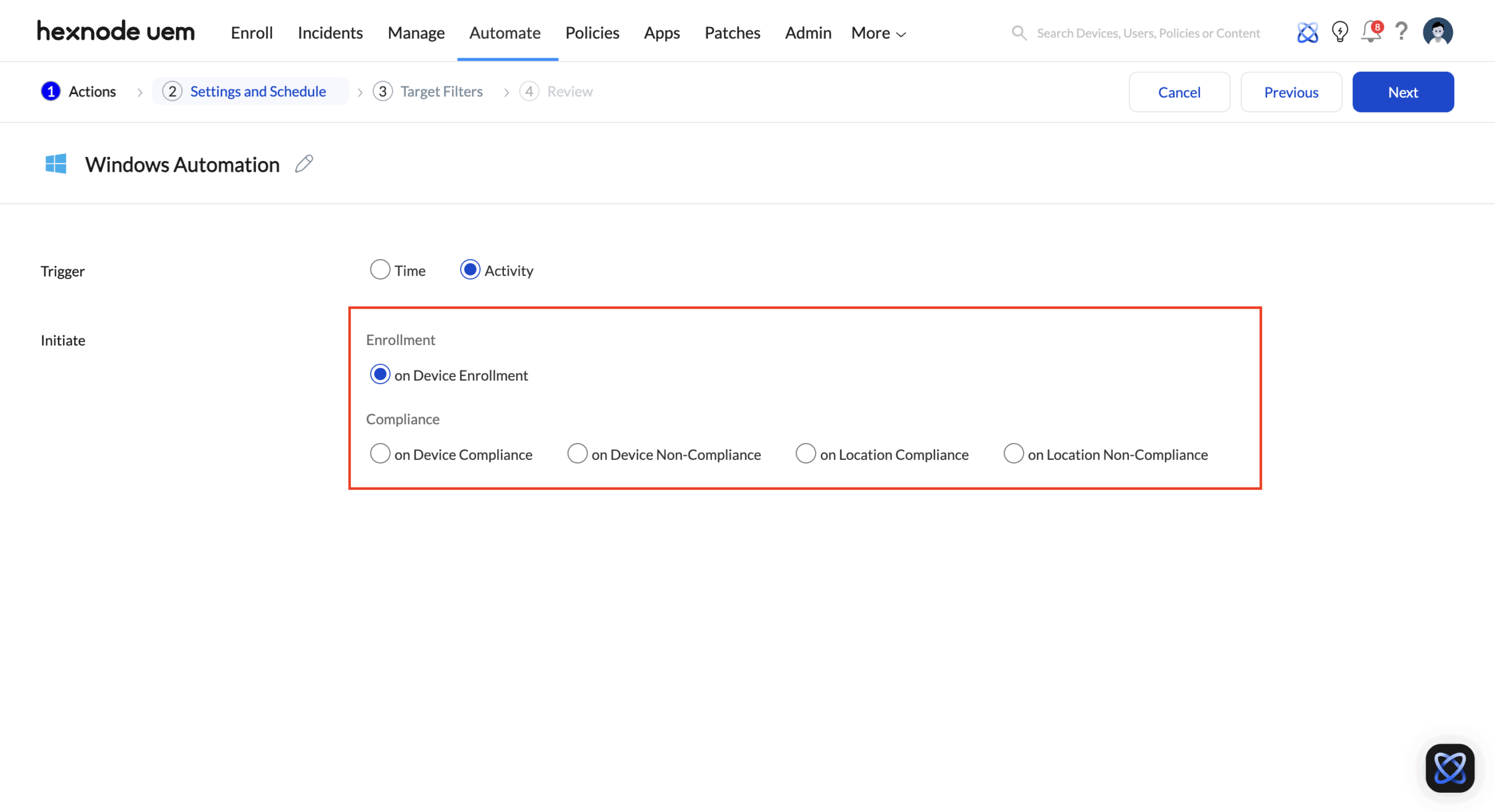
Navigation: Automate > New Automation > [Platform] > Settings and Schedule > Triggers > Activity
The Automate tab is designed around device-level state transitions. These triggers observe changes in enrollment status, compliance posture, location context, and device activity. Automation is initiated when a device crosses a defined threshold or enters a new state.
| Event (Trigger) | Description | Enterprise Use Case and Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| On Device Non-Compliance | Triggers instantly when a device violates a policy (e.g., unauthorized app installed, security settings tampered). | Zero-Tolerance Security: The workflow immediately Forces a Device Lock, sends a non-compliance email to the user, and Associates a highly restrictive policy, effectively quarantining the compromised device until the issue is resolved. |
| On Device Enrollment | Triggers immediately after a new user completes the enrollment process. | Automated Onboarding: The workflow automatically associates the required Security Policy, deploys the VPN Profile, and installs a bundle of 10+ Required Enterprise Applications (like CRM and Email clients). |
| On Location Compliance/Non-Compliance | Triggers when a device enters or leaves a predefined Geofence (e.g., leaving a secure facility). | Dynamic Policy Switching: When a high-security warehouse tablet leaves the Geofence (Non-Compliance), the workflow automatically activates Lost Mode and performs a Corporate Data Wipe after a set delay. |
| On Device Inactive | Triggers when the device has not checked in with the server for a specified duration (e.g., 72 hours). | Lost Asset Protocol: Executes a workflow that sends a final user warning and then automatically performs a Corporate Wipe to secure sensitive data on lost or stolen devices. |
Lifecycle-Based automation through Scripts policy
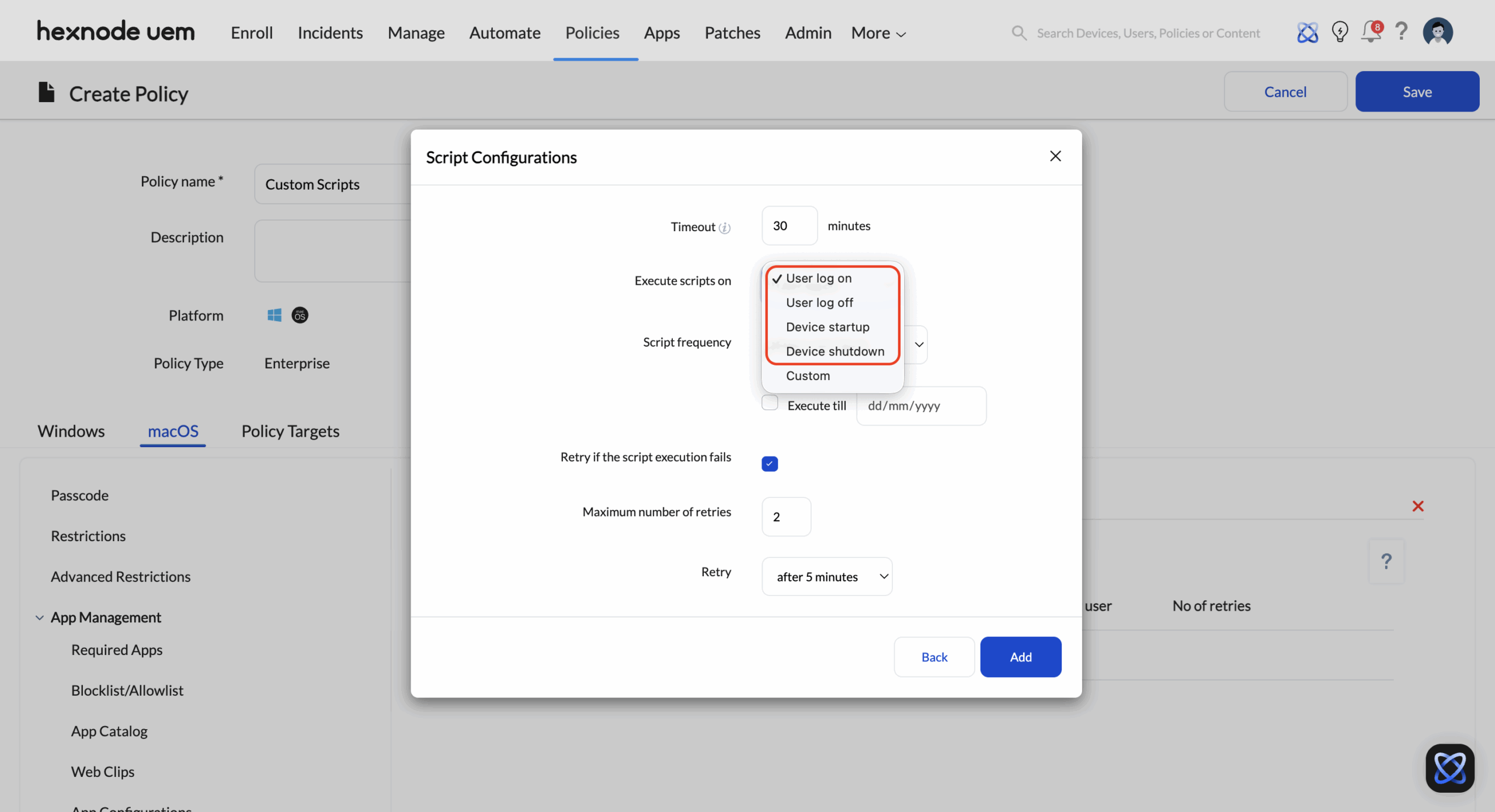
Navigation: Policies > Device Policy > New Policy > Platform (macOS or Windows) > Enterprise > Configurations > Scripts
While device-state automation focuses on fleet-wide conditions, Scripts policy operate closer to the operating system and user session lifecycle. These triggers are tied to predictable system and user events, making them suitable for enforcing consistency at the start or end of each session.
| Event (Trigger) | Description | Enterprise Use Case and Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| On User Logon (Windows and macOS) | Triggers at the moment a user successfully signs in to the device. The automation is tied to the start of an active user session rather than to the device state alone. | Session-Ready Work Environment: The workflow prepares the user workspace by validating security posture, ensuring required applications and network resources are available, and applying session-specific configurations. This guarantees that every login begins from a controlled and standardized state without relying on always-on enforcement. |
| On Device Startup (Windows and macOS) | Triggers when the operating system boots, before any user interaction occurs. The automation executes at the system level. | Pre-Login Compliance Assurance: Enterprises use this trigger to perform system validation, apply baseline security configurations, and run maintenance tasks. Devices are fully prepared and compliant before users log in, reducing delays and preventing policy drift during active sessions. |
| On User Logout and Shutdown (macOS) | Triggers when a user logs out of their session or when the device initiates shutdown. The automation aligns with session termination rather than device inactivity. | Session Cleanup and Data Isolation: In shared or shift-based environments, workflows remove residual user data, reset configurations, and revoke temporary access. This ensures that each session remains isolated, preventing data leakage and maintaining a consistent starting state for the next user. |
The Power of Automation Workflows
The action triggered by the event is not limited to a single command. Hexnode’s Automate feature allows for complex bundling of actions, making the response sophisticated and targeted.
Key Actions Within a Workflow
- Policy Management: Associate or Remove multiple policies dynamically.
- Remote Actions: Execute critical, time-sensitive commands like Corporate Wipe, Lost Mode, and Lock Device.
- Script Execution: Run pre-configured Custom Scripts (PowerShell, Bash) for deep configuration, patch verification, or forensic data collection.
- Notifications: Send automated email or SMS alerts to both the user and the administrator, ensuring accountability and communication.