Category filter
Simplifying Enterprise Application Delivery: Hexnode’s Approach to Deploying Win32 apps
Overview
Microsoft Intune has the concept of Win32 app packaging to enable deployment of traditional Windows applications using a unified deployment model. This model combines installers, scripts, detection logic, and dependency handling into a single operational unit, commonly distributed as an .intunewin package.
Hexnode approaches the same deployment challenges using a configuration driven enterprise app model for Windows, where application logic is defined directly during app configuration rather than embedded into a wrapped package.
This document maps Intune’s Win32 app concepts to Hexnode’s Windows enterprise app capabilities, helping administrators understand how equivalent deployment outcomes can be achieved without a dedicated wrapping tool.
Understanding the Intune Win32 App Model
An Intune Win32 app consists of:
- An installer payload (EXE, MSI, or scripts)
- Optional pre or post execution logic
- Detection logic to confirm installation state
- Dependency relationships between applications
- Installation behavior controls such as context, retries, and restarts
The Win32 Content Prep Tool packages these components into a single .intunewin file so Intune can deliver and execute them via the Intune Management Extension.
Hexnode’s Windows Enterprise App Deployment Model
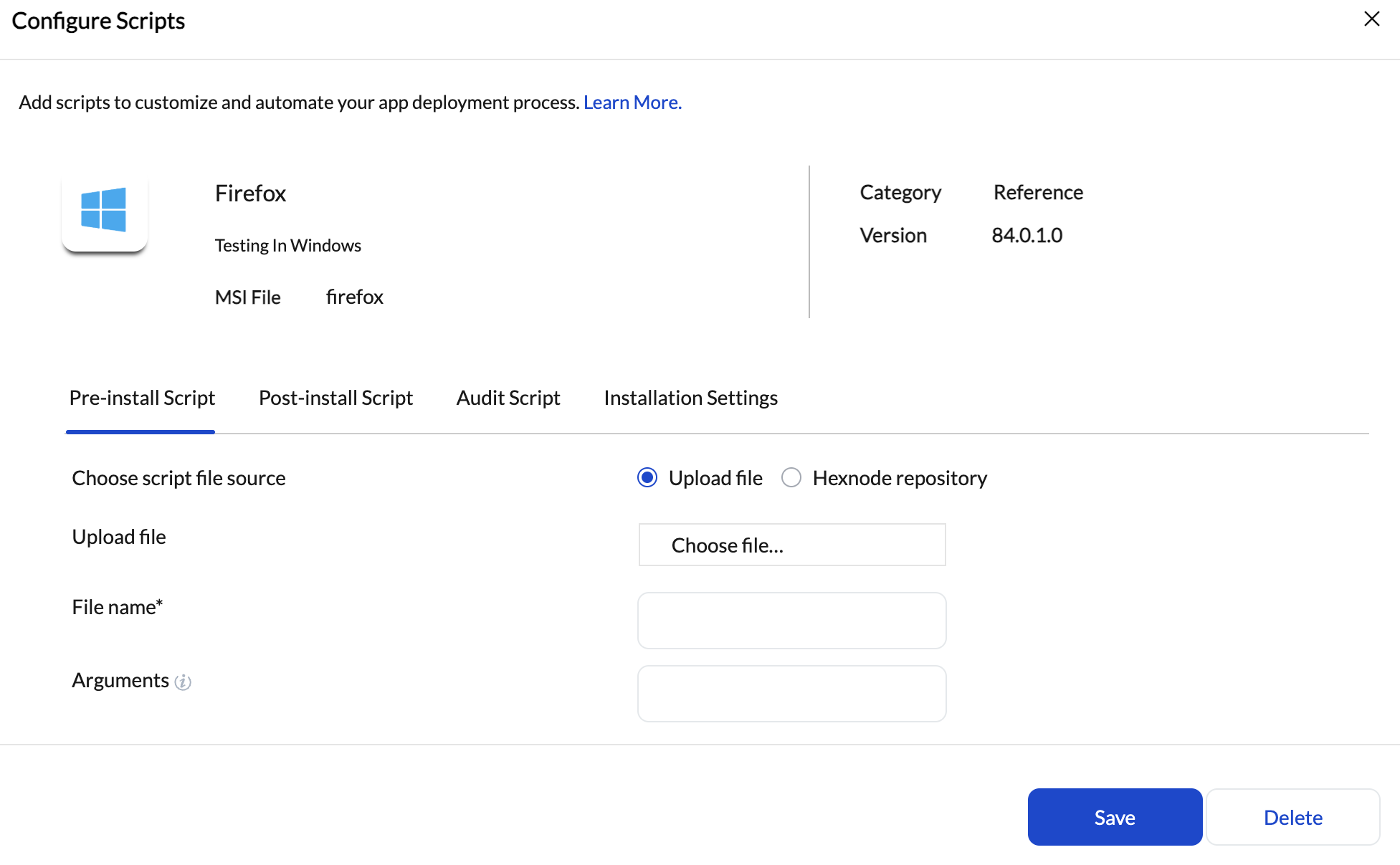
Hexnode enables deployment of Windows enterprise applications by allowing administrators to associate scripts, installers, and execution logic directly with the application configuration.
Instead of embedding logic into a packaged container, Hexnode separates concerns:
- Application content is uploaded as-is
- Execution logic is defined declaratively
- Validation and auditing are handled through scripts
- Installation behavior is controlled through configurable parameters
This model removes the need for an offline packaging or wrapping workflow while still supporting complex enterprise deployment scenarios.
Conceptual Mapping: Intune Win32 Apps vs Hexnode Windows Enterprise Apps
Application Packaging
| Intune Win32 Apps | Hexnode |
|---|---|
| Requires conversion of app source files into .intunewin | No proprietary packaging format is required |
| Uses a command line content prep tool | Installers and scripts are uploaded directly |
| Logic and content are tightly coupled inside the package | Deployment logic is configured within the platform |
Key takeaway: No command-line wrapping tool required. Application logic is defined at configuration time rather than embedded into a package.
Installer Execution
| Intune | Hexnode |
|---|---|
| Installer commands are defined during Win32 app configuration | Installer execution is defined as part of the enterprise app configuration |
| Execution is triggered by the Intune Management Extension | Supports EXE based application deployment with controlled execution |
Both platforms ultimately execute native installers on the device. The difference lies in where that execution logic is authored.
Pre-install and Post-install Logic
Intune
-
Pre and post logic is typically embedded using scripts referenced by the install command or included in the package
Hexnode
- Pre-install and post-install scripts are explicitly defined as part of the app configuration
- Scripts execute in sequence around the installer
This makes deployment flow visible and adjustable without rebuilding application packages.
Detection and Validation
| Intune | Hexnode |
|---|---|
| Detection rules or scripts determine whether the application is installed | Audit scripts evaluate installation state and system conditions |
| Detection governs retries, compliance, and reporting | Audit results provide validation and visibility into deployment outcomes |
Both approaches rely on script-based evaluation rather than installer return codes alone.
Dependencies and Conditional Execution
| Intune | Hexnode |
|---|---|
| Dependencies are defined between Win32 apps | Conditional logic can be implemented using pre-install or audit scripts |
| Applications install in a required sequence based on dependency rules | Script based checks can control whether installation proceeds |
While Intune models dependencies as a formal relationship, Hexnode enables equivalent outcomes through script driven validation and sequencing.
Installation Behavior and Controls
| Intune | Hexnode |
|---|---|
| Installation context, restart behavior, and retries are defined per Win32 app | Installation settings provide control over execution behavior |
| Changes often require repackaging or reconfiguration | Additional parameters can be adjusted without modifying the installer payload |
This supports faster iteration when deployment behavior needs refinement.
Architectural Difference, Not Capability Loss
Intune encapsulates application logic inside a wrapped package.
Hexnode externalizes application logic into configuration and scripts.
Both models:
- Execute native Windows installers
- Support pre and post execution logic
- Validate installation success
- Enable controlled enterprise scale deployment
Hexnode’s approach avoids the operational overhead of maintaining a packaging pipeline while preserving functional parity for most Windows enterprise application use cases.
Summary for Migration Planning
When migrating from Intune Win32 apps to Hexnode:
- The .intunewin file is replaced by direct installer uploads
- Detection rules map to audit scripts
- Embedded scripts map to pre and post install scripts
- Dependencies are handled through conditional execution logic
- Installation behavior is controlled through configurable settings
The result is the same deployment outcome, achieved through a different architectural approach.