Category filter
Streamlining CVE Remediation: How to Automate Patching from Detection to Fix
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures, or CVEs, are standardized identifiers used to describe publicly known security flaws in operating systems and applications. For IT and security teams, identifying which CVEs affect their devices is only valuable if it directly leads to timely remediation.
Hexnode UEM addresses this by combining native vulnerability visibility with patch intelligence and automation. CVEs detected across enrolled Windows devices are continuously surfaced, mapped to the patches that resolve them, and made actionable within the same platform.
Rather than treating vulnerability scanning and patch deployment as separate workflows, Hexnode links CVE identification directly to patch availability and deployment readiness. Administrators can not only view affected devices and associated CVE details, but also automate patch deployment based on specific CVE criteria.
This approach allows organizations to move from vulnerability awareness to automated remediation, ensuring that devices are patched as soon as relevant CVEs are identified, without relying on external security tools or manual intervention.
Elevating Vulnerability Management as a Solution
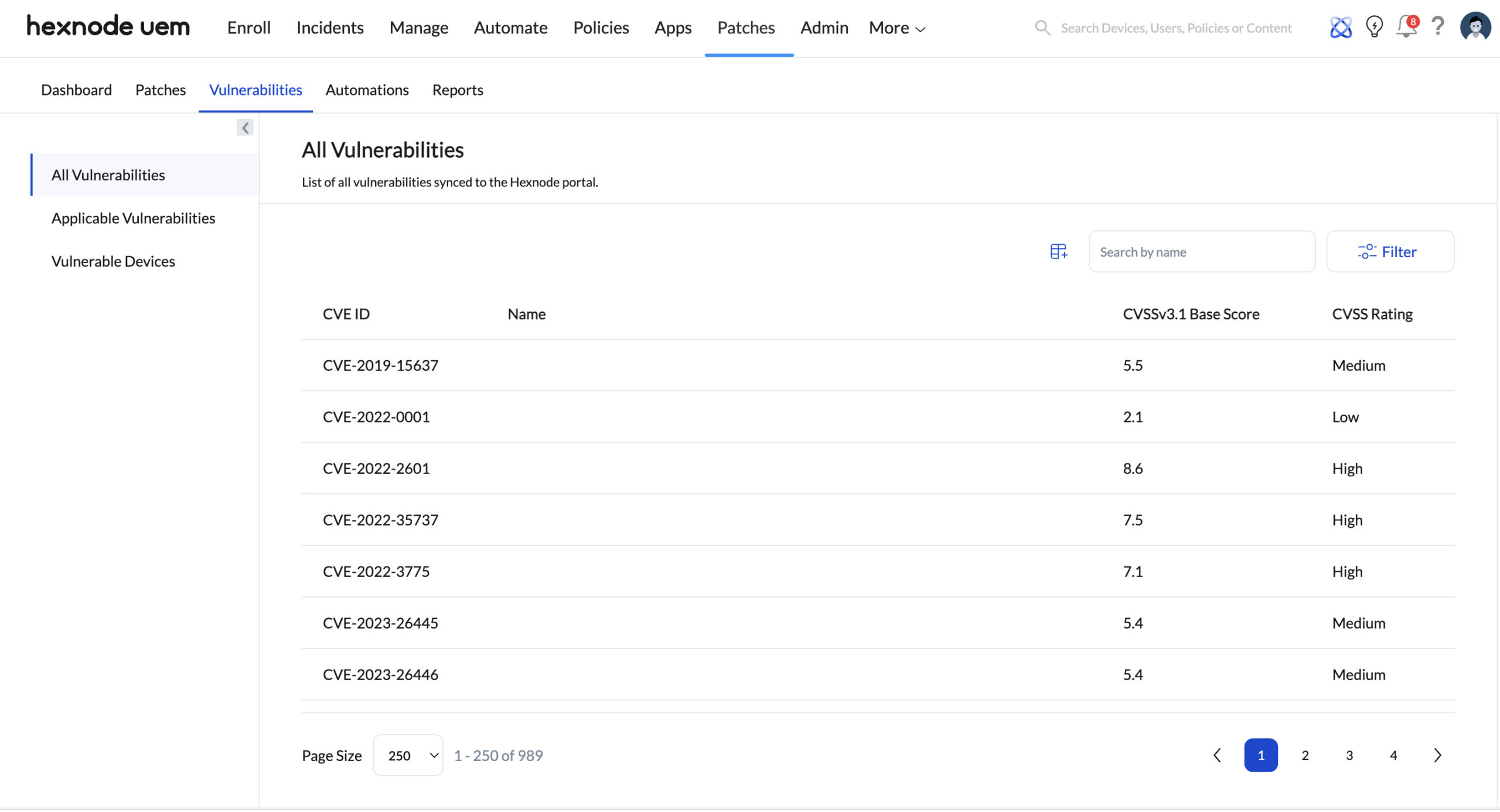
Under the Patches section in Hexnode UEM, vulnerability data is displayed through a dedicated Vulnerabilities sub-tab.
This view consolidates:
- All CVEs detected across enrolled Windows devices
- The CVSSv3.1 Base Score and CVSS rating associated with each vulnerability
- The list of affected devices where the vulnerability is applicable
What matters here is not just visibility, but traceability.
From CVE Awareness to Patch Context
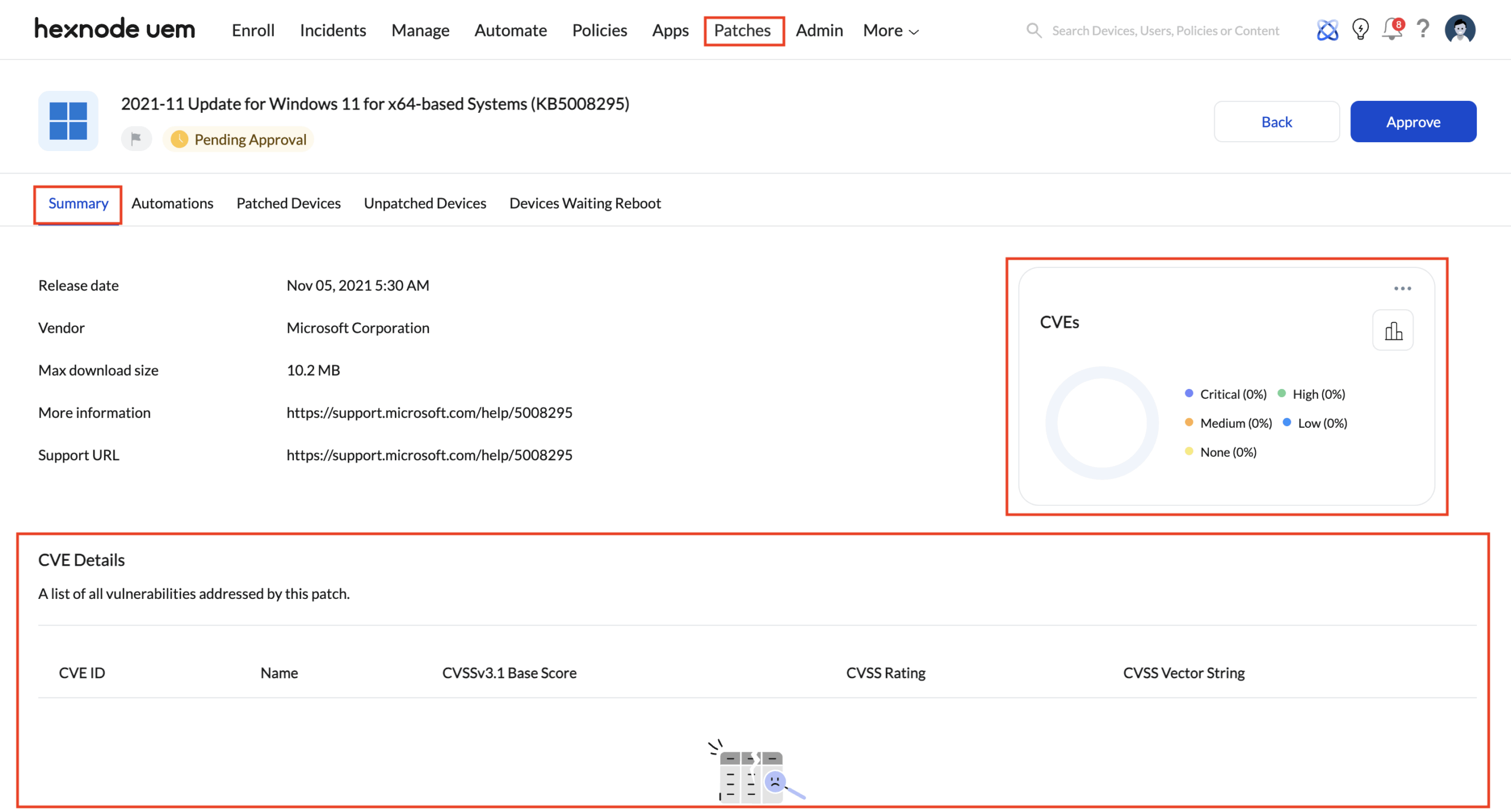
Every available patch in Hexnode carries its vulnerability metadata with it.
Each vulnerability shown is directly tied to one or more available patches. When an admin navigates to Patches > Available Patches and inspects a patch, the associated CVEs are clearly listed as part of that patch’s context.
This means CVE awareness and patch readiness exist in the same decision space, not across disconnected tools.
This creates a direct mapping:
- CVE identifier
- Impacted software or OS component
- Vulnerabilities addressed by this patch
Closing the Loop with Native Automation
Identifying CVEs is only half the battle. The real operational gain comes from ensuring they are addressed consistently, without manual triage every time a new vulnerability surfaces.
Creating a CVE-Based Auto Patch Automation
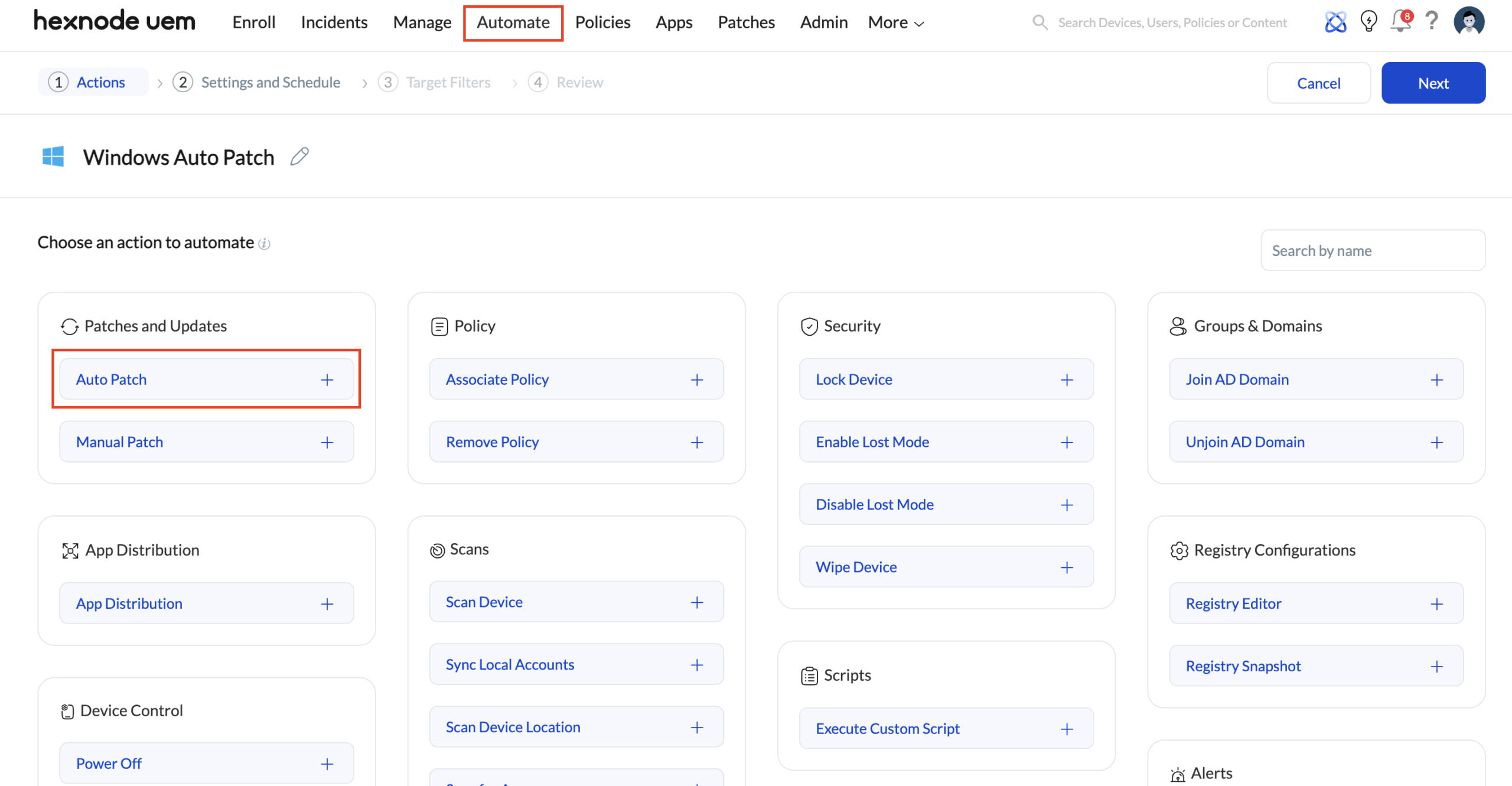
To automate patch deployment based on identified vulnerabilities, administrators can create an auto-patching workflow from the Automate tab in Hexnode UEM.
Navigate to the Automate tab in the Hexnode portal and select New Automation.
- Under Active Automations, choose Windows as the platform.
- Provide a name for the automation to reflect its purpose, such as CVE-based patch remediation.
- In the Patches and Updates section, select Auto Patch and click the + option to include it as an automation action.
This establishes the automation framework where patch deployment decisions will be driven by vulnerability data.
Configuring Patch Criteria Using CVEs
Once the automation action is added, patch eligibility can be defined using CVE-based conditions.
- Under Update Criteria, Select Windows as the update type to manage operating system updates.
- Choose CVEs as the evaluation column.
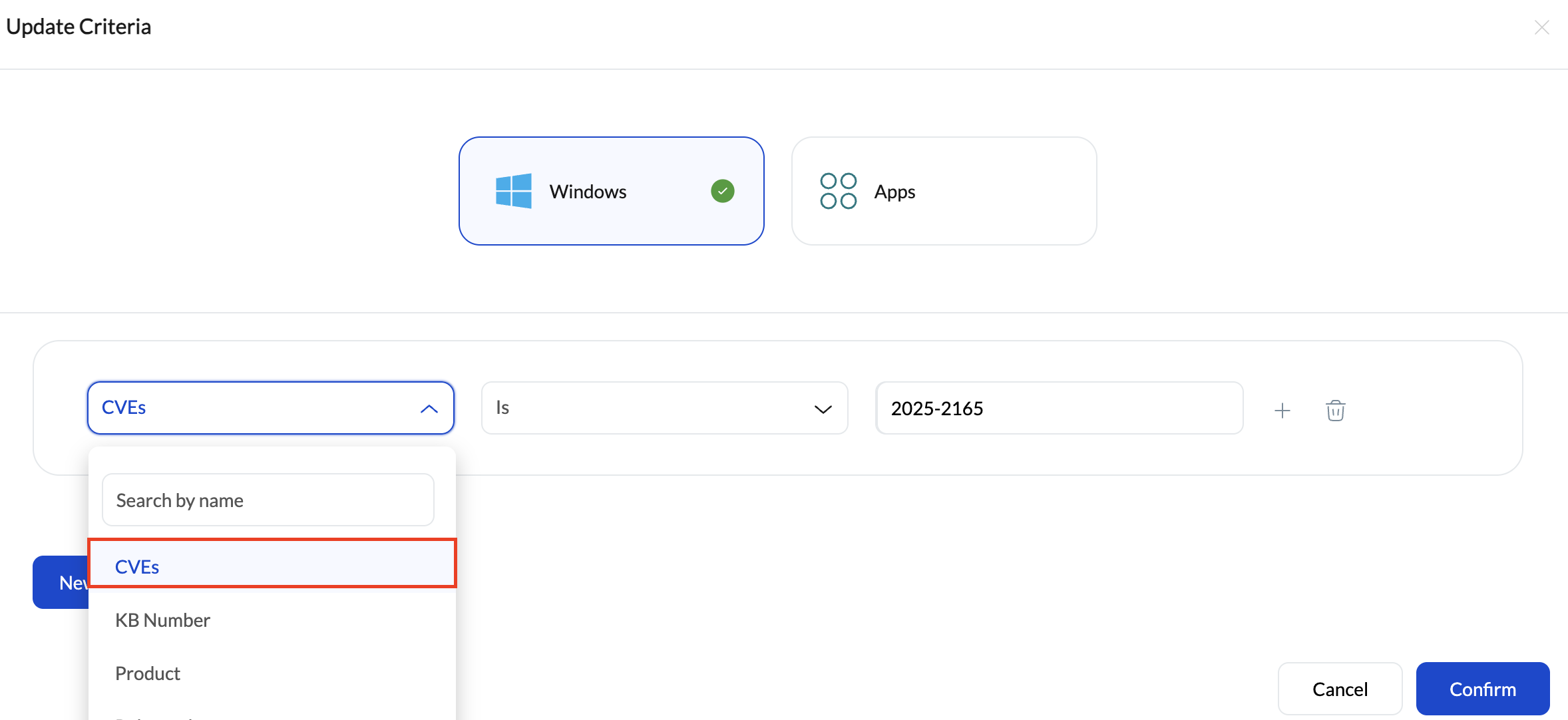
- Select a suitable comparator based on how vulnerabilities should be matched.
- Provide the required CVE identifier or value to define which vulnerabilities the automation should respond to.
By using CVEs as the primary condition, the automation evaluates patches based on the vulnerabilities they remediate, rather than relying on patch names or release schedules.
Finalizing Automation Settings and Deployment Scope
After defining the CVE-based criteria, additional preferences can be configured to align the automation with organizational requirements.
- Optional settings such as updates to ignore, automation rules, and device-end notifications can be enabled as needed.
- Configure the schedule to determine when patch deployment evaluations and actions should occur.
- Select the target endpoints where the automation should apply.
- Review all configured settings to ensure accuracy and alignment with patching policies.
Once confirmed, create the automation to activate continuous CVE-driven patch deployment across the selected devices.
This shift patching from a reactive workflow to a proactive one.
Why this matters for Security Teams?
This flow removes a common misconception: that native CVE visibility requires external security integrations.
In Hexnode UEM:
- CVEs are natively scanned and surfaced
- Vulnerabilities are directly linked to remediating patches
- Patching decisions can be automated based on CVE criteria
The result is a streamlined vulnerability management lifecycle that lives entirely within the UEM platform.
Analysts do not need to export vulnerability lists, correlate them elsewhere, or manually chase remediation steps. Visibility, decision-making, and action remain tightly coupled.
The Takeaway
Hexnode’s approach treats vulnerability management not as a reporting feature, but as a continuous remediation workflow.
By embedding CVE analysis inside the patching ecosystem and extending it into automation, Hexnode enables teams to:
- Identify vulnerabilities at scale
- Understand exactly how they are remediated
- Enforce patching automatically based on CVE exposure