Category filter
Create custom configuration profiles for Windows
This document will help you create custom configuration profiles for Windows devices.
Windows Configuration Service Providers (CSPs) allows admins to read, set, modify, or delete configuration settings on the device. MDM service providers use CSPs for management tasks and policies for Windows devices. To define these policies, administrators use payloads, which are specific settings or configurations communicated to a device to adjust its behavior or settings. These payloads, typically delivered via configuration profiles, can be used to manage various aspects of a device, such as security, networking, or application settings.
With Hexnode’s Deploy Custom Configuration feature, administrators can create custom configuration profiles using payloads and deploy them across managed Windows devices.
Creating custom configuration profile
To create a custom configuration profile for Windows via policy,
- Log in to the Hexnode UEM console.
- Navigate to Policies > New Policy.
- Provide a policy name and description (optional).
- Go to Windows > Configurations > Deploy Custom Configuration and click on Configure.
- Click on Enable atomic execution to ensure the payloads within the policy is applied entirely.
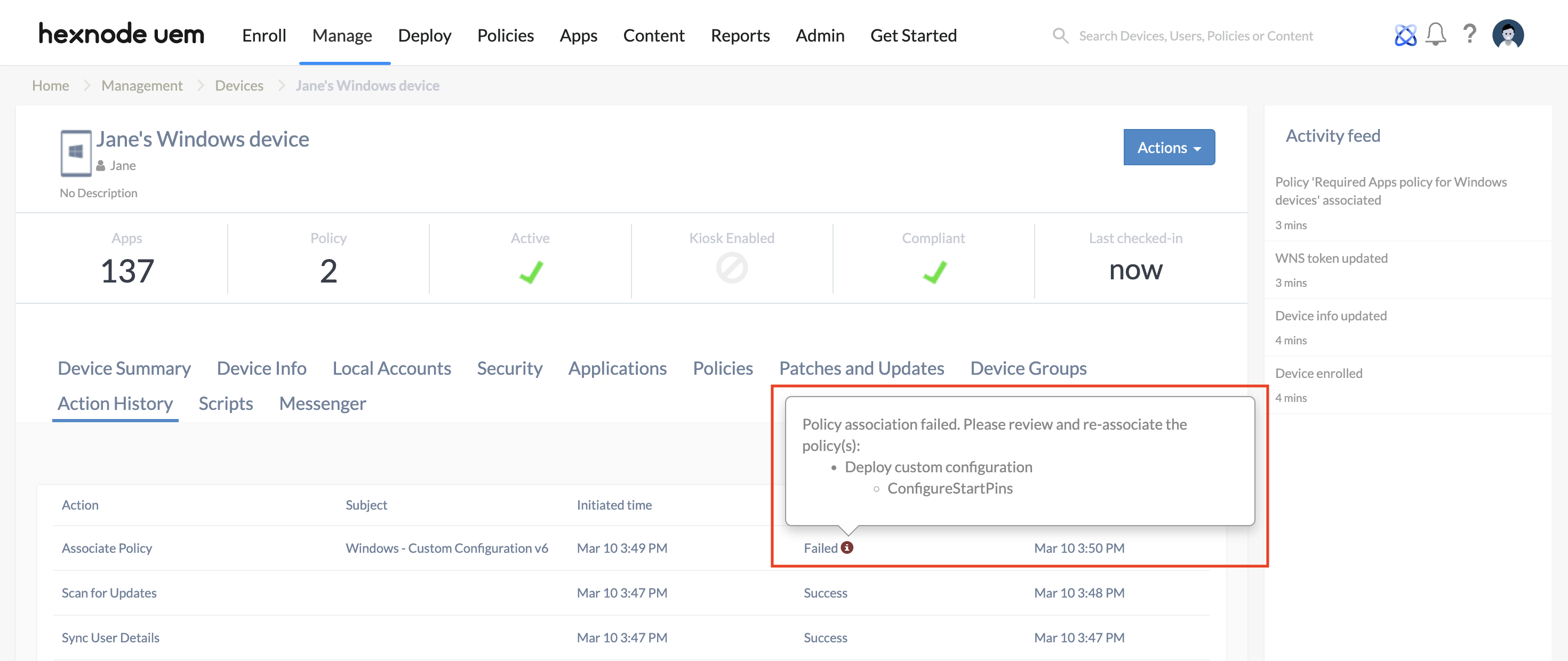
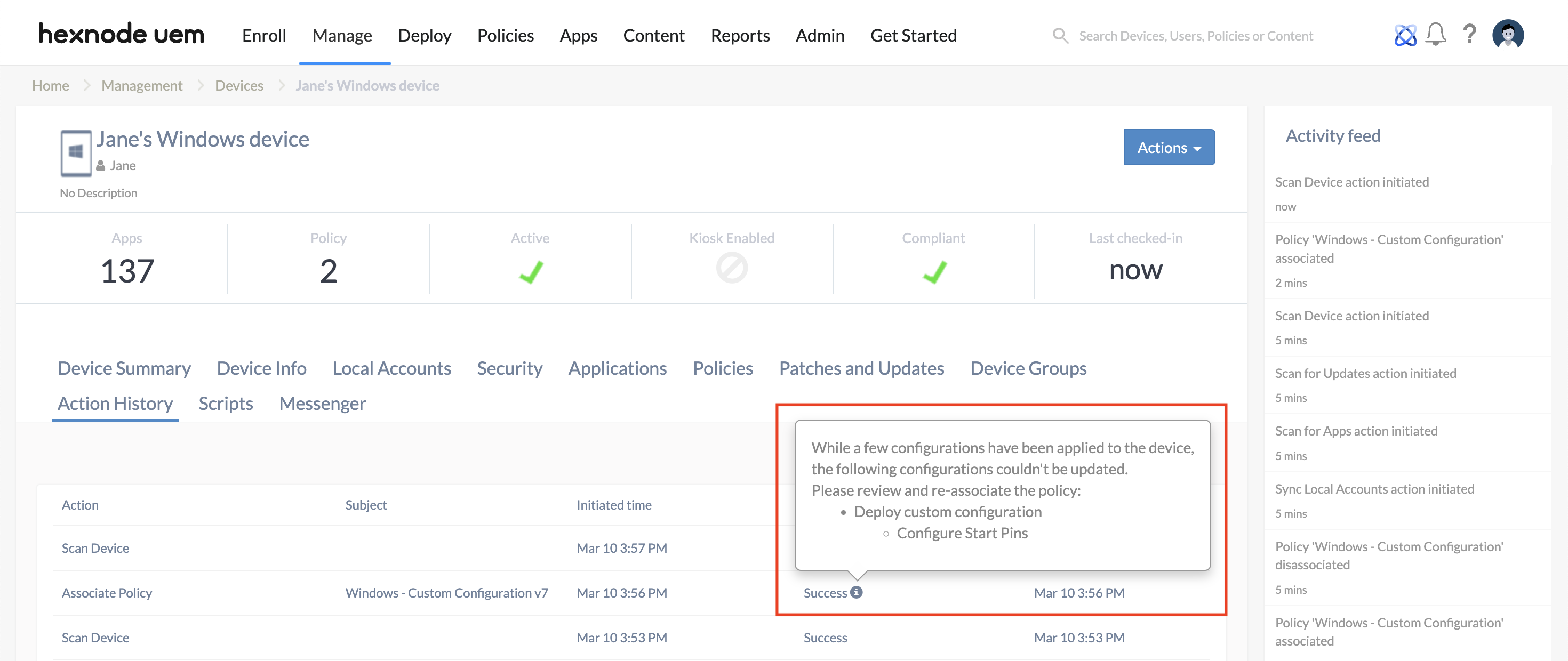
Since multiple payloads can be configured within a single policy, enabling this setting ensures that all custom payloads configured within the policy will either be successfully applied together or fail as a unit. If failure of any payload occurs, the policy will be marked as Failed in the Action History, with an information icon indicating the payload causing the error.
When the setting is disabled, and if failure of any paylaod occurs, the action will be marked as Success in the Action History with the information mentioning the payload causing the error. Only the payload having the error will fail, rest of the payloads will be successfully applied.
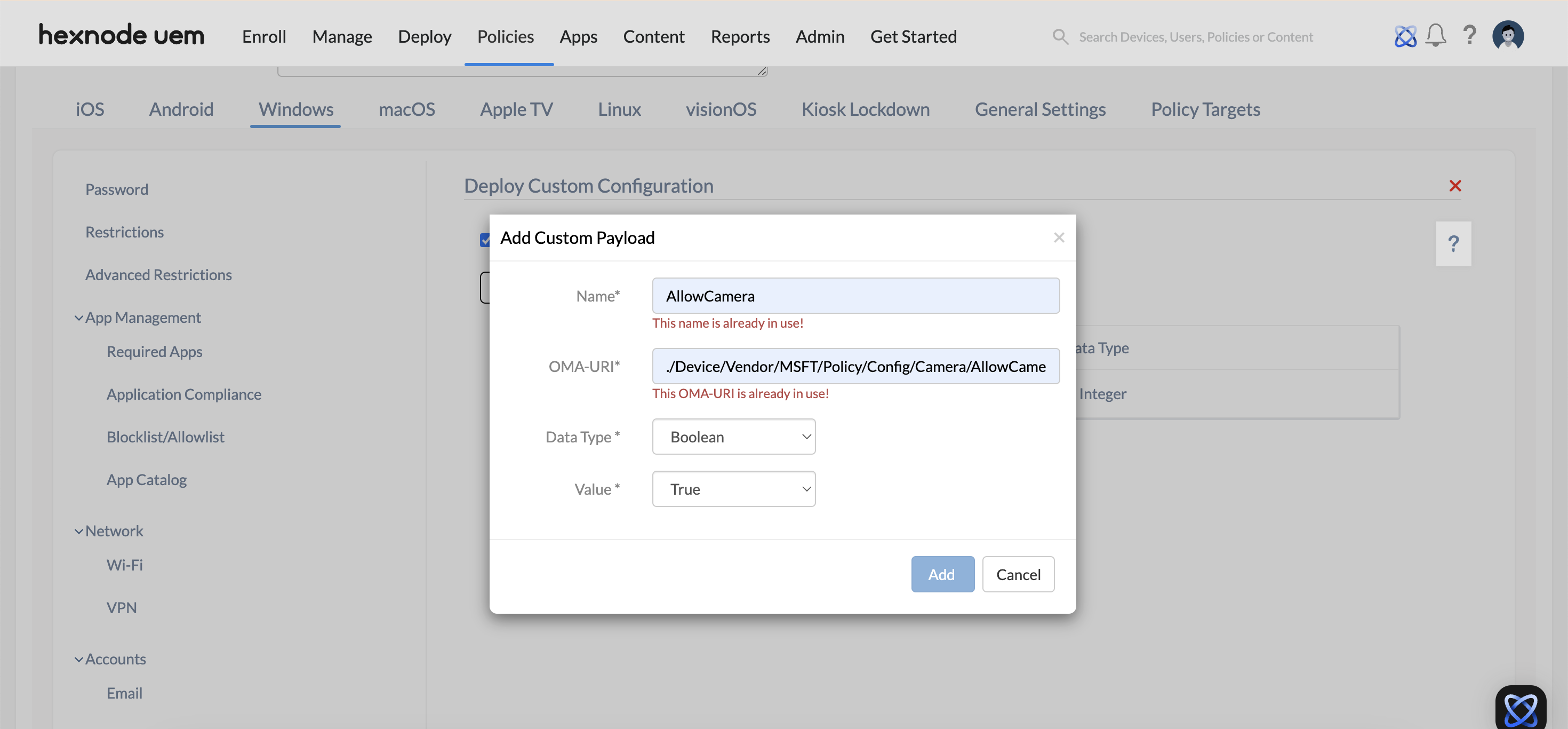
- Click on Add Payload to add custom payload and configure the settings below.
- Name: Provide a name for the custom payload. This is a required field.
- OMA-URI: Specify the OMA-URI (Open Mobile Alliance – Uniform Resource Identifier), which is a distinct path to a configuration setting supported by a CSP. This is a required field.
For example, the OMA-URI for the usage of camera on the device would be, ./Device/Vendor/MSFT/Policy/Config/Camera/AllowCamera.
- Data Type: Choose the data type for the custom payload. Options include Boolean, String, String (XML), or Integer formats.
- Value: Enter a value based on the selected data type format. This field is required.
- For Boolean, choose between True or False.
- For String, input a custom value.
- For String (XML), upload an XML file.
- For Integer, provide a numeric value.
For example, the value for integer data type for the usage of camera would be, 1 for allowed, and 0 for not allowed.
- Associate the policy to the target devices by navigating to Policy Targets > +Add Devices.
- Select the target devices and click OK.
- Click Save.
What happens at the device end?
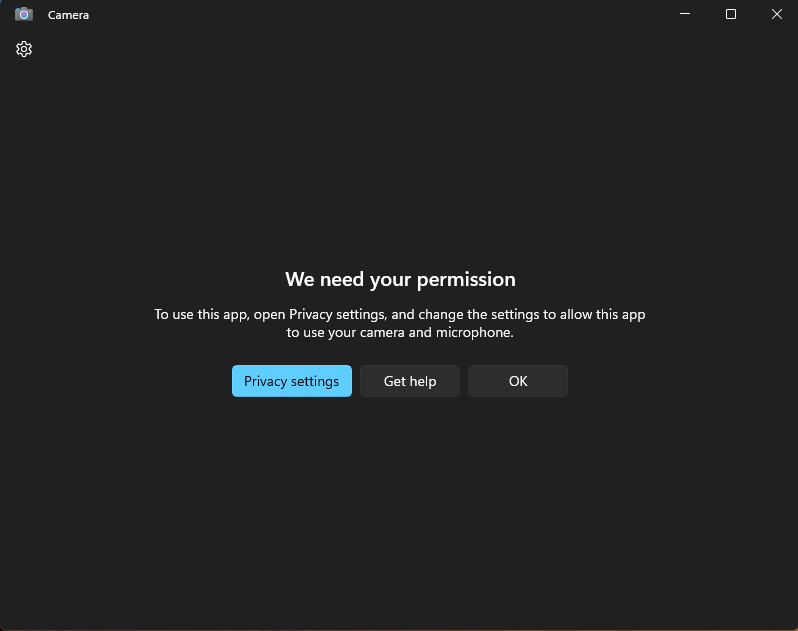
The specific payload that has been configured will take effect on the device. For example, if the payload is set to disable camera access, the camera will be disabled on the Windows device.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
1. What is the difference between the “./Device” and “./User” paths in an OMA-URI?
The prefix of the OMA-URI defines the scope of the configuration. Payloads beginning with ./Device apply globally to the endpoint regardless of which user is authenticated. Payloads starting with ./User are specific to the individual managed user profile and only take effect when that specific user is logged into the device.
2. Are OMA-URI strings case-sensitive?
Yes. Administrators must ensure that the OMA-URI path exactly matches the casing specified in Microsoft’s CSP reference. Incorrect casing (e.g., using ./device/ instead of ./Device/) will result in the device being unable to locate the target node, leading to a deployment failure.
3. Is it possible to use wildcards within the “Value” field of a custom payload?
No. Unlike some Hexnode policies (such as Email or VPN), the “Value” field for custom configuration payloads does not support wildcards. The administrator must provide the exact literal value required by the CSP.
Troubleshooting
1. Error Code 404: Not Found
Probable Cause:
The administrator has entered an incorrect OMA-URI path, or the target setting is not supported by the specific Windows edition (e.g., attempting to apply an Enterprise-only CSP to a Pro edition device).
Solution:
Verify the OMA-URI string against the official Microsoft CSP reference and confirm that the device is running a supported Windows edition and version for that specific node.
2. Status: ‘Failed’ with Atomic Execution Enabled
Probable Cause:
A single payload within a multi-payload policy has encountered an error, causing the entire “Atomic” block to fail and roll back all other settings to maintain system consistency.
Solution:
Inspect the Action History of the device and click the information icon to identify the specific payload causing the conflict. The admin may need to isolate the problematic payload into a separate policy for further testing.
Best Practices
- Pilot Testing: The admin should always deploy new or complex custom configurations to a small pilot group of devices before an organizational rollout to identify potential OS-level conflicts.
- Validate via Diagnostic Reports: If a policy fails silently, the admin should use the Advanced Diagnostic Report on the Windows device (Settings > Accounts > Access work or school > Info) to verify which OMA-URI settings were successfully processed by the local MDM engine.