Category filter
Script to install PowerShell on Windows
What is PowerShell?
PowerShell is a cross-platform task automation and configuration management framework that includes a command-line shell and scripting language, designed to work across cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments. On Windows systems, there are two distinct versions of PowerShell: Windows PowerShell and PowerShell 7+.
Windows PowerShell, version 5.1, is preinstalled on all modern Windows client and server operating systems. It uses the executable powershell.exe. In contrast, PowerShell 7+, which uses the executable pwsh.exe, is not preinstalled on any version of Windows and must be installed manually.
How to install PowerShell 7 on managed Windows devices?
Admins can install PowerShell 7 on Windows devices using multiple methods, including WinGet, an MSI installer, a ZIP package, the .NET global tool, the Microsoft Store, or custom scripts.
The choice of installation method depends on factors such as administrative permissions, network setup, and whether the installation is for a single device or for multiple devices across an organization.
For remote deployment at scale, administrators can use Hexnode’s Execute Custom Script action. This feature allows them to run installation scripts on multiple devices simultaneously, making it easy to install PowerShell 7 or upgrade the existing version across Windows endpoints.
How does Hexnode simplify PowerShell deployment?
While the Execute Custom Script action provides a convenient way to run installation scripts on target devices, IT admins can also deploy scripts through the Scripts policy for periodic execution and more structured rollouts.
Alternately, these actions can be automated to trigger during specific events such as device enrollment, or can be scheduled to run during maintenance windows by specifying the date, day and time.
In this walkthrough, we will focus on the various commands and scripts available for installing or upgrading PowerShell 7 on Windows.
Scripts to Install or Upgrade PowerShell 7 via Hexnode
Installing PowerShell using MSI installer
The following script can be used to deploy PowerShell via Hexnode:
|
1 2 3 4 |
$msiUrl = "https://example.com/path/to/PowerShell-installer.msi" $msiPath = "$env:TEMP\PowerShell-7.4.1-win-x64.msi" Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $msiUrl -OutFile $msiPath Start-Process msiexec.exe -ArgumentList @( "/i "$msiPath"", "/quiet", "/norestart", "ADD_PATH=1", "ENABLE_PSREMOTING=1", "ADD_EXPLORER_CONTEXT_MENU_OPENPOWERSHELL=1", "ADD_FILE_CONTEXT_MENU_RUNPOWERSHELL=1", "REGISTER_MANIFEST=1" ) -Wait |
How does the script work?
This script downloads the PowerShell MSI installer from the specified URL to the device’s temporary folder. Replace the $msiUrl value with the URL that corresponds to your device architecture, such as x64, x86, or arm64. It then performs a silent installation using the /quiet option, which runs the installer without user interaction, and the /norestart option to prevent automatic restarts.
Several installation options are enabled by default to enhance the PowerShell experience:
- ADD_PATH=1
Adds PowerShell to the system PATH, making it easier to launch from any command prompt or script. - ENABLE_PSREMOTING=1
Enables PowerShell remoting and configures to receive remote commands. - ADD_EXPLORER_CONTEXT_MENU_OPENPOWERSHELL=1
Adds a convenient option to open PowerShell directly from the File Explorer context menu. - ADD_FILE_CONTEXT_MENU_RUNPOWERSHELL=1
Provides a context menu option to quickly run PowerShell scripts from File Explorer. - REGISTER_MANIFEST=1
Registers the PowerShell application manifest to complete and integrate the installation properly.
Upgrading PowerShell using MSI installer
To upgrade PowerShell 7, run the same installation script with the updated MSI download URL and file name. The Windows Installer will automatically replace the existing version with the new one.
Device end behaviour:
When the installation script is executed via Hexnode, PowerShell 7 is silently installed in the background on the Windows device, without any user interaction.
Commands to Install or Upgrade PowerShell 7 on Windows
Install PowerShell using WinGet
WinGet (Windows Package Manager) is a command-line utility that helps users find, install, upgrade, remove, and configure applications on Windows systems. The following commands can be used to install PowerShell using the winget packages. These commands are typically run directly by admin users within Windows PowerShell on the device.
- To search for the latest PowerShell versions:winget search Microsoft.PowerShell
This command searches the WinGet repository for available PowerShell versions and lists them.
- To install PowerShell using the package ID: winget install –id Microsoft.PowerShell –source winget
This command installs the latest PowerShell version from the WinGet repository using the specified package ID, i.e., Microsoft.PowerShell.
Upgrading PowerShell using WinGet
WinGet can also be used to upgrade PowerShell to the latest version. The commands below are typically run directly by admin users in Windows PowerShell on the device itself.
- To check if a newer version of PowerShell is available for upgrade, run the following command:
winget list –id Microsoft.PowerShell –upgrade-availableThis command lists the installed PowerShell version and indicates if an upgrade is available, showing the latest version, you can install.
- If an upgrade is available, use the following command to perform the upgrade:
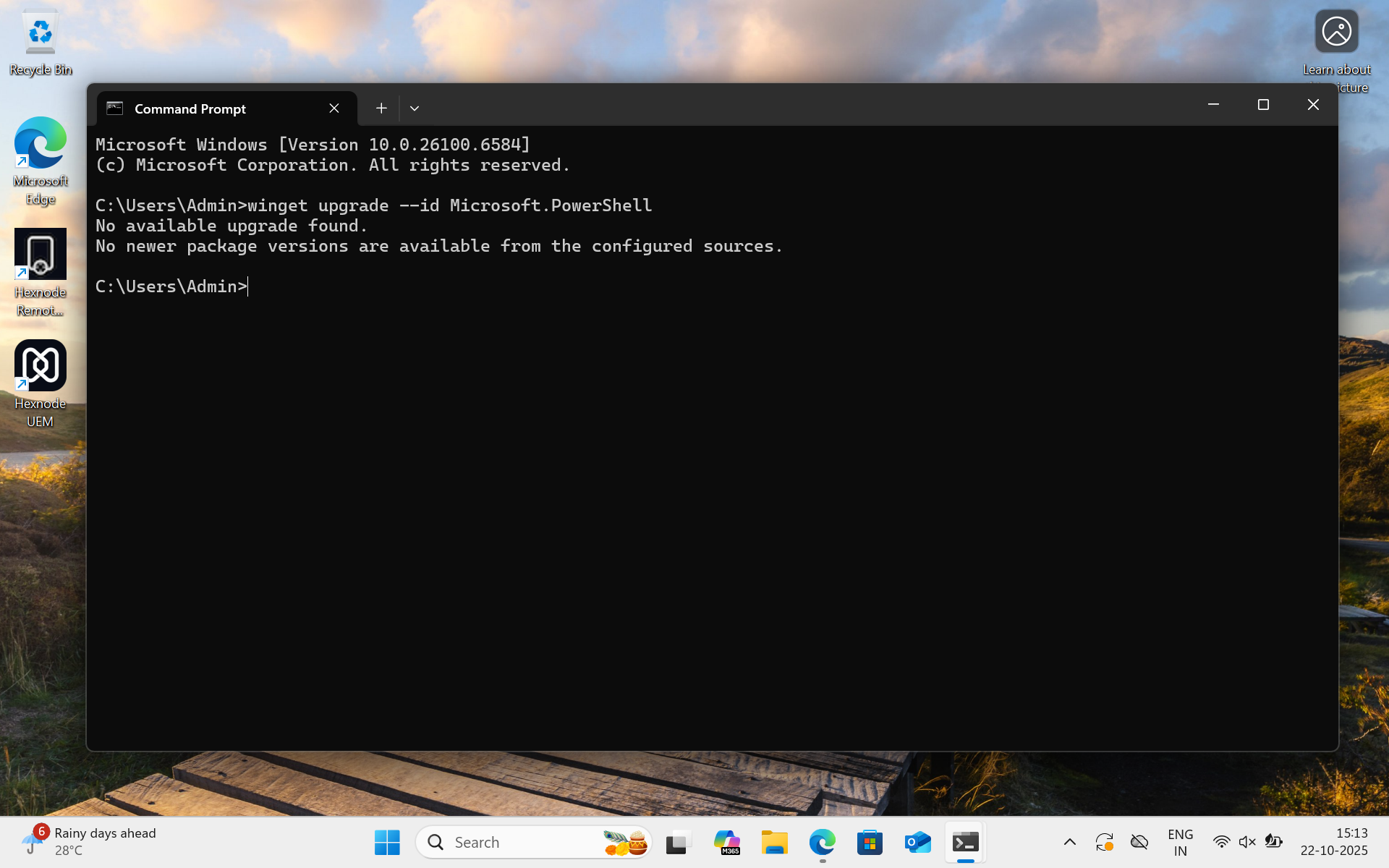
winget upgrade –id Microsoft.PowerShellThis command downloads and installs the latest version of PowerShell available from the WinGet repository.
Device end behaviour:
When the command to upgrade PowerShell is run on the device, it checks for available updates and returns the message “No available upgrade is found.” if the installed version is already up to date.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
- Can PowerShell 7 and Windows PowerShell be used on the same device?
Yes, PowerShell 7 can be installed alongside Windows PowerShell 5.1 on the same device. They use different executable names (pwsh.exe for PowerShell 7 and powershell.exe for Windows PowerShell), allowing them to coexist without conflict.
- How can it be determined if PowerShell 7 is already installed on a Windows device?
Administrator users can launch the Command Prompt and type pwsh. If PowerShell 7 is installed, it will display the version number. Alternatively, open PowerShell and run $PSVersionTable.PSVersion to check the installed version.
You can also run the following PowerShell script through Hexnode to check whether PowerShell 7 is installed on a device.12$pwshPath = Get-ChildItem 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall' | ForEach-Object { Get-ItemProperty $_.PSPath } | Where-Object { $.DisplayName -like 'PowerShell *' -and $.DisplayName -notlike 'Windows PowerShell' }if ($pwshPath) { Write-Host "PowerShell 7 is installed: $($pwshPath.DisplayName)" } else { Write-Host "PowerShell 7 is NOT installed." } - Does PowerShell 7 support all Windows versions?
PowerShell 7 is supported on the following Windows operating systems:
- Windows 10 and Windows 11
- Windows Server 2016, 2019, and 2022