An Update to Cybersecurity with Hexnode MDM
For enterprises betting everything on securing their systems, Zero Trust is an unavoidable update for cybersecurity.

Get fresh insights, pro tips, and thought starters–only the best of posts for you.
Andrei Geralt
Feb 5, 2021
8 min read
What is the one thing you know which keeps others from accessing any of your accounts? Well, there are many ways to keep your account secure, but password authentication is what probably came to your mind. Using a password might seem reliable but after taking a look at the statistics, you might start having second thoughts on the matter.

Since most enterprises are trying to digitalize everything, hackers can find almost anything when a data breach occurs. If you’d like to think, ‘who would bother to hack into my device?’ or ‘Nobody would want to hack my system’, then here’s a fact. One in every three Americans get hacked every year! A Clark study at the University of Maryland revealed that hackers are accessing devices with network access every 39 seconds on average. On top of that, Interpol had reported an increase in cybercrimes after the onset of the pandemic. Cybercrimes were rampant with phishing attacks contributing to 94% of Covid related cyber-attacks across a two week period. “Rather than fearing or ignoring cyber-attacks, do ensure your cyber resilience to them.” said Stephane Nappo, Global CISO, Société Générale. Most organizations seem to be having the same idea and have started allocating resources for cybersecurity. By 2023, About $6 trillion is being anticipated to be globally invested in cybersecurity. This may seem like an exaggerated reaction, but then again nobody wants to take the risk of being breached. Still not convinced? Cybersecurity Ventures estimates a 15% increase in cybercrime costs for the next few years, projecting a whopping $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. Now it makes sense, right?

MFA is pretty much used to log into most domains. It’s weird how we probably didn’t notice this even when we were authenticating using factors like entering OTPs and answering security questions. Multi-Factor Authentication sometimes referred to as two-factor authentication or 2FA, is an authentication technique where more than one factor (exactly two in the case of 2FA) is demanded to verify the identity of the user before he/she can access an online account, a VPN, an application, or the data on a mobile device. MFA is considered to be a crucial component of Identity Access Management (IAM). In any typical scenario, we only need the credentials such as username and password in order to get past security and gain access. But if MFA is implemented, we need two or more factors for user verification. It can belong to any of the three categories; something you know (which can be a pin or password), something you have (like an MS authenticator or smart card), or something you are (that is, biometrics).
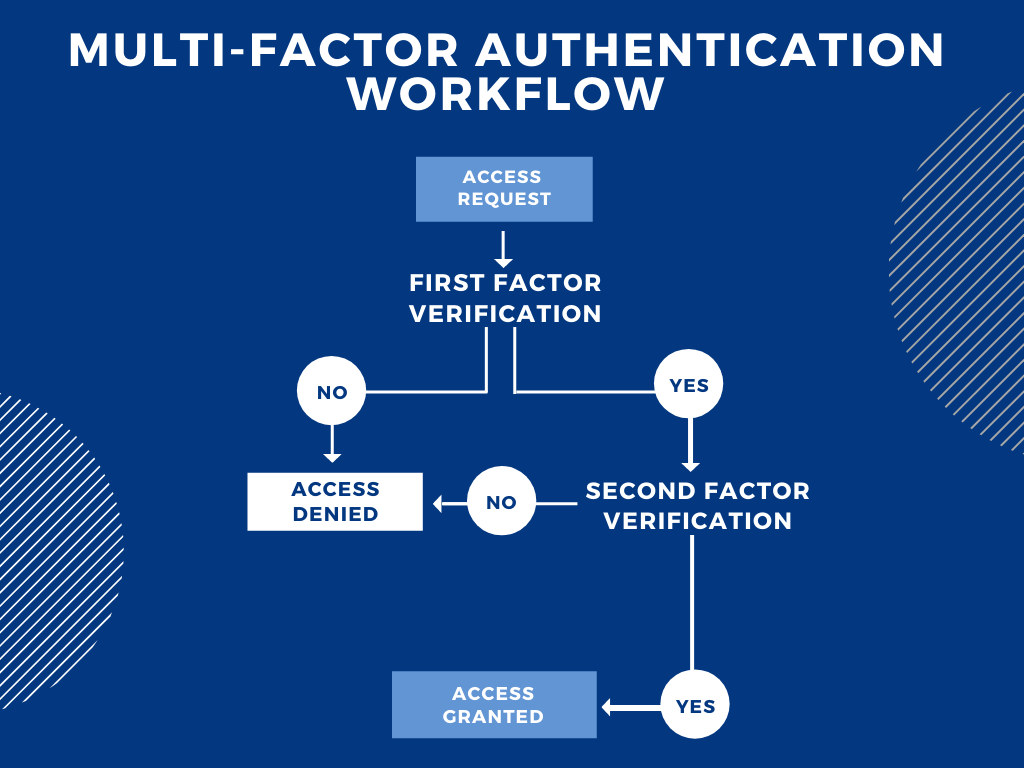
Suppose something urgent comes up and you have to access your work account from home. When you click on ‘login,’ an access request gets sent, and another page pops up asking for your login credentials. These credentials would be the first factor for authentication, that is, the first evidence you present which can vouch for your identity. Suppose you messed up your password the first time and were denied access. So, you tried again and got it right this time. Let’s say the next factor is an OTP, which, if entered right, would grant you access to the account; else, you’d be denied access again. By implementing more factors for verification, the security would be greatly enhanced.
While password authentication is one layer of protection, Multi-Factor Authentication provides more than one layer of protection. The more, the better right? Obtaining the credentials of a person is possible, but credentials and their device? More unlikely. What about their credentials, device, and fingerprint? Highly unlikely. Using Multi-Factor authentication reduces the chances of data breaches significantly when compared to password authentication. If somebody is very determined to hack into your device, you might have to get more layers of security, but in most cases, MFA would suffice.
While employing MFA all the time seems like a great idea, it could be cumbersome to keep trying to prove who you are. What if you only need to verify your identity only once if the context is always the same? Well, it isn’t exactly an ‘if’ since the concept of adaptive MFA already exists. Adaptive/ Contextual or Risk-based MFA is used to optimize the customer’s or the employee’s convenience while maintaining security. During low-risk situations, the organization might choose to decrease security or even bypass MFA. In high-risk scenarios, the level of security would increase, especially in high-value transactions. Any MFA utilizing a context verification step can also be referred to as Contextual MFA.

So, does MFA really contribute much to cybersecurity? So here are some more statistics. About 99.9% of the Microsoft accounts that got hacked weren’t secured with MFA, which means almost no Multi-Factor Authenticated accounts were hacked. Accounts with MFA have more security so, in case your credentials get stolen during a mass hack or data breach, your account will remain secure. MFA is also very popular with almost all personal and professional platforms. Social media, enterprise, gaming platforms have all decided to switch to MFA to the point where it has already become an integrated part of our lives. With its simple deployment, enhanced security, and popularity, the real question is, why haven’t you set up MFA already?
Share your thoughts