How Windows 11 makes Hybrid work a breeze
Windows facilitates hybrid work by introducing features that specifically aim at enhancing remote working conditions.

Get fresh insights, pro tips, and thought starters–only the best of posts for you.
Wayne Thompson
Jun 6, 2023
27 min read
Windows 11 security is a top priority in the latest version of the Windows operating system. In October 2021, Microsoft released Windows 11, a highly secure and efficient operating system that surpasses its predecessors in terms of security and performance. Windows 11 introduces a wide array of new security features and enhancements, positioning it as one of the most secure operating systems currently in existence.
Amidst the increasing prevalence of cyber-attacks, it is crucial to give priority to securing your Windows 11 device by configuring its security settings. This ensures comprehensive protection against potential threats. So, the Windows 11 security team has meticulously crafted new features that add extra layers of protection, effectively thwarting potential attacks. These security options include enhanced hardware-based security, secure boot, virtualization-based security, and Windows Hello, which allows users to use biometric authentication for secure login.
In addition to the built-in security features, there are other security measures that users can take to protect their Windows 11 devices. One of the most crucial steps is to configure app permissions properly. Users should only allow apps to access the minimum required data and functions, preventing apps from accessing sensitive data. Furthermore, it is essential to use a strong password or PIN to prevent unauthorized access. Enabling automatic updates ensures that the latest security patches and updates are installed, keeping the device secure.
Windows 11 hardware security utilizes a combination of hardware and software-based security measures, such as Microsoft Pluton, TPM, Windows Defender System Guard, and Kernel DMA protection, to protect against a wide range of cyber threats and unauthorized access. These features work together to establish a trusted boot process, measure the integrity of firmware and hardware components, and isolate the system from malicious software and untrusted devices.
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a critical component of Windows 11 security. TPM is a microchip that stores critical system information, such as encryption keys, passwords, and digital certificates, and provides hardware-level security to protect against tampering and unauthorized access. Windows 11 supports TPM 2.0, which includes advanced security features such as remote attestation, secure boot, and key storage.
Currently, Microsoft integrates the security processor, Microsoft Pluton, directly into the CPU. This processor serves as a hardware root of trust, safeguarding both devices and data. Pluton encompasses essential functions such as a secure boot process, generation of cryptographic keys, and secure storage. The secure boot process guarantees a secure system boot, while cryptographic key generation and storage enable reliable data encryption and decryption. Additionally, Microsoft Pluton offers the capability to function as a TPM (Trusted Platform Module). This means that Windows 11 devices that come with Pluton do not require a separate TPM chip, simplifying the design of devices while providing the same level of security.
Windows Defender System Guard is a suite of security features that protect against firmware-level attacks. It includes Secure Boot, Secure Launch and Memory Integrity. Secure Boot actively prevents malicious software from loading during the startup of your PC, Secure Launch protects against firmware attacks during system startup, and Memory Integrity helps protect against kernel-level attacks that try to tamper with system memory. Additionally, Windows Defender System Guard provides a hardware-based root of trust to help protect against attacks that target the firmware. It uses Secure Root of Trust Measurement (SRTM), Dynamic Root of Trust Measurement (DRTM), and System Management Mode (SMM) to protect against firmware attacks and rootkits. These technologies establish a trusted boot process, measure the integrity of firmware and hardware components, and isolate the system from malicious software.
Finally, Kernel DMA protection is a Windows 11 feature that helps to protect against Direct Memory Access (DMA) attacks over Thunderbolt. It works by using a combination of software and hardware-based security measures to isolate the system from untrusted devices and prevent unauthorized access to the system’s memory.

Get started with Hexnode’s Windows Management solution to improve security, increase productivity, save time and overhead costs of managing your corporate devices.
Download the datasheetMicrosoft offers resources and tools to assist developers in writing secure code, performing rigorous testing, and implementing secure configurations for software applications. By prioritizing software security, organizations can enhance the overall resilience of their systems and safeguard sensitive information from potential threats.
Windows incorporates essential security features known as Secure Boot and Trusted Boot to provide protection against unauthorized and malicious software. Secure Boot guarantees that solely trusted and digitally signed operating system components are loaded during the boot process, effectively preventing the execution of unauthorized or tampered code. Trusted Boot extends this protection by verifying the integrity of key system files during the boot process, ensuring the system starts with a known and secure state. By leveraging Secure Boot and Trusted Boot, organizations can enhance the security and integrity of their Windows devices, mitigating the risk of boot-time attacks and unauthorized modifications to the system.
BlackLotus malware bypasses Windows Secure Boot: Tips to maximize security
To access the Secure Boot and Trusted Boot settings, users can navigate to the device’s UEFI or BIOS settings during the boot process. It is highly advisable to enable these features as they significantly enhance the device’s security by verifying the integrity and authenticity of the operating system and crucial system files.
Cryptography and certificate management play a vital role in securing data and communications. Microsoft offers robust cryptographic services and tools for Windows that enable organizations to implement encryption, digital signatures, and secure communication protocols. These cryptographic capabilities ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of sensitive information. Additionally, Microsoft provides guidance on certificate management, including best practices for certificate issuance, revocation, and renewal. By effectively managing certificates and leveraging cryptographic services, organizations can establish a strong foundation for securing their Windows environments and protecting critical data from unauthorized access and tampering.
They can be accessed and configured through the Windows Certificate Manager or Microsoft Management Console (MMC). IT admins should establish and enforce policies for cryptography and certificate management, define standards for encryption algorithms and key lengths, and ensure proper management and renewal of certificates.
The Windows Security app is another Windows 11 security feature that serves as a centralized hub for managing and monitoring the security of the devices. It provides a comprehensive set of tools and features to protect against threats and vulnerabilities. Furthermore, the app offers real-time threat detection and removal through Windows Defender Antivirus, safeguarding devices from malware, viruses, and other malicious software. It also includes features such as firewall management, device health monitoring, and ransomware protection. With the Windows Security app, users can easily access and manage various security settings, ensuring that their Windows devices are protected against evolving threats.
Encrypting sensitive data is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and protect confidentiality. Microsoft offers robust encryption and data protection features for Windows devices. BitLocker, a built-in encryption tool, provides full-disk encryption, ensuring that even if a device is lost or stolen, the data remains secure. It utilizes strong encryption algorithms and secure key management to protect data at rest. In addition to BitLocker, Microsoft also provides options for encrypting hard drives and personal data. These encryption capabilities enable organizations to safeguard their sensitive information, maintain compliance with data protection regulations, and mitigate the risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access.
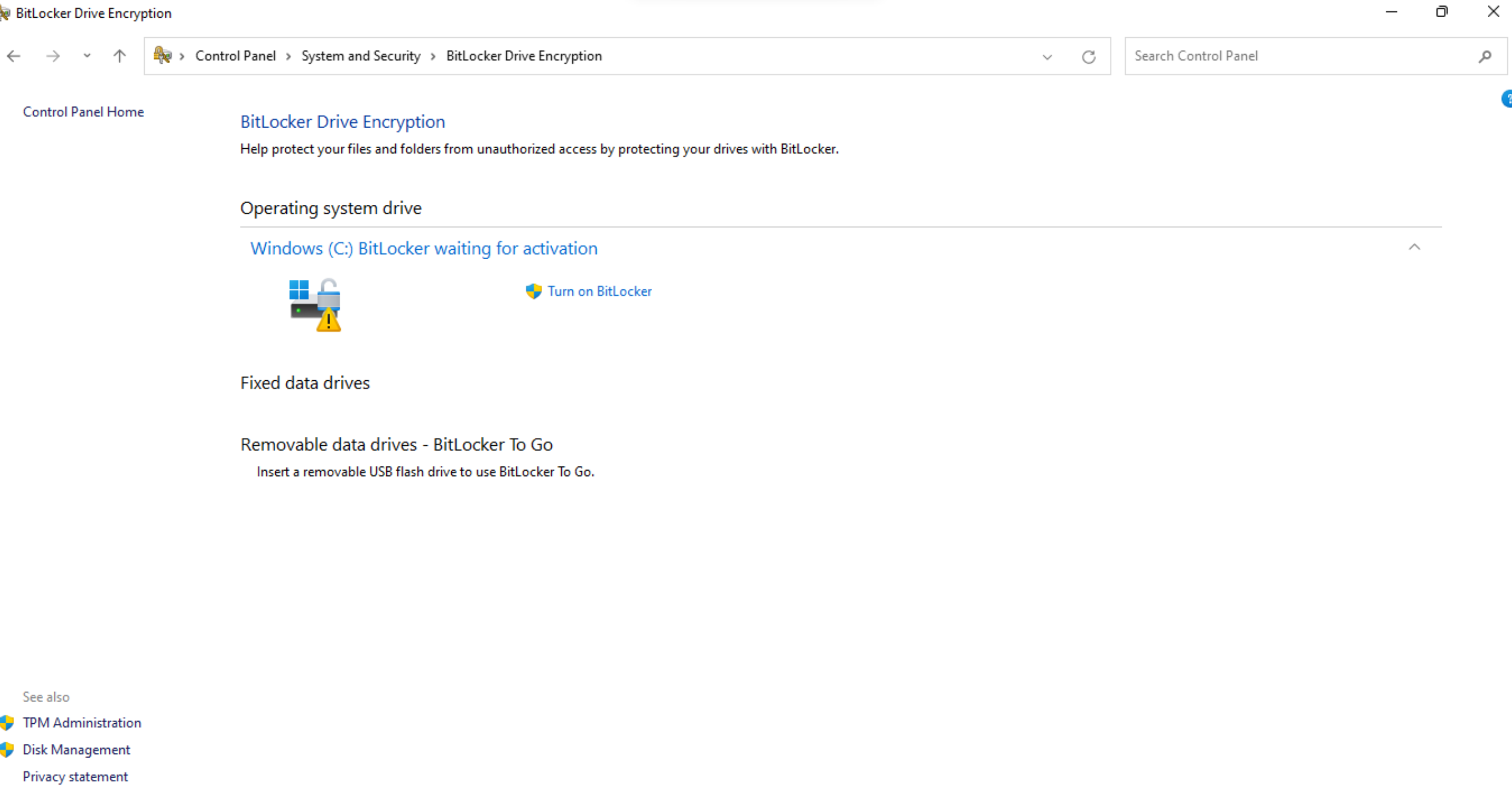
Windows Defender Firewall is a built-in security feature in Windows that protects devices from unauthorized network traffic and potential threats. It offers advanced security functionalities to control inbound and outbound network connections, ensuring that only trusted traffic is allowed. Microsoft provides detailed information on Windows Defender Firewall, including its various configuration options and advanced security settings. Administrators can leverage these resources to understand how to customize firewall rules, create exceptions for specific applications or ports, and manage firewall profiles effectively. By utilizing Windows Defender Firewall, organizations can fortify their devices against network-based attacks and unauthorized access attempts, bolstering the overall security posture of their Windows environment.
Accessible through the Windows Security app or Control Panel, it provides network protection by controlling inbound and outbound connections. IT admins should ensure that Windows Defender Firewall is enabled and properly configured on Windows devices within the organization. They should define firewall rules based on security requirements, monitor and log firewall activities, and regularly update firewall configurations.
Protecting Windows devices from malware and other malicious software is paramount in maintaining a secure computing environment. Microsoft Defender Antivirus, the built-in security solution for Windows, offers comprehensive protection against a wide range of threats. It utilizes real-time scanning, behavioral analysis, and cloud-based threat intelligence to detect and remove malware from devices. Microsoft provides valuable resources on Microsoft Defender Antivirus, including information on its features, configuration options, and best practices for optimal protection. Administrators can leverage these resources to ensure that Microsoft Defender Antivirus is properly deployed and configured to provide robust antivirus and antimalware protection to Windows devices, safeguarding against emerging threats and minimizing the risk of infections.
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is an essential tool for maintaining secure and private connections, especially when accessing networks remotely. Microsoft provides comprehensive guidance on VPNs, including a guide that covers the basics of VPN technology, its benefits, and best practices for implementation. The guide highlights different VPN connection types, such as point-to-site and site-to-site and offers insights into choosing the right VPN solution for specific requirements. By following Microsoft’s recommendations, organizations can establish secure VPN connections, encrypt data transmission, and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or interception.
From an IT admin’s perspective, they should provide guidelines on using VPNs, configure VPN settings and connection types based on organizational needs, and ensure secure and reliable VPN connections for remote workers.

Minimizing the attack surface of Windows devices is crucial in reducing the risk of security breaches. Microsoft Defender Endpoint provides attack surface reduction rules that help organizations strengthen their defenses. These rules employ various techniques to block or mitigate known attack vectors and techniques used by malicious actors. By implementing attack surface reduction rules, organizations can enforce strict control over executable files, scripts, and potentially harmful activities, reducing the likelihood of successful attacks. Microsoft offers comprehensive documentation on attack surface reduction rules, enabling administrators to understand the available rules and effectively configure them to enhance the security posture of their Windows devices.
IT admins should implement attack surface reduction rules to mitigate risks, define and enforce rules based on organizational security requirements, and regularly review and update the rules to adapt to evolving threats.
Preventing unauthorized changes to security settings is vital in maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of security measures. Microsoft Defender Endpoint offers tamper protection features that safeguard Windows devices against unauthorized modifications. With tamper protection enabled, critical security settings, such as antivirus configurations and firewall rules, are protected from tampering by unauthorized users or malicious software. Microsoft provides detailed guidance on enabling and configuring tamper protection, allowing organizations to strengthen their security defenses and ensure that security settings remain intact and effective.
It is suggested that IT admins should centrally manage and configure tamper protection settings, regularly review tamper protection logs, and respond to any tampering attempts promptly.
Network protection is a crucial aspect of overall endpoint security. Microsoft Defender Endpoint offers network protection capabilities that safeguard Windows devices from network-based attacks and malicious traffic. It leverages various technologies, such as network filtering and machine learning-based analysis, to identify and block suspicious network communications. Microsoft provides comprehensive information on network protection, including its features, configuration options, and best practices. Organizations can strengthen their Windows devices against network threats and improve overall security by implementing network protection measures. This minimizes the risk of compromise through network-based attacks.
Controlled folder access is a powerful security feature provided by Microsoft Defender Endpoint. It helps protect sensitive data by controlling which applications can access and modify specific folders. With controlled folder access enabled, unauthorized applications are prevented from making changes to protected folders, mitigating the risk of unauthorized data access or tampering. Microsoft offers detailed documentation on configuring and managing controlled folder access, enabling organizations to define and enforce strict access controls for sensitive data. By leveraging controlled folder access, organizations can strengthen data protection, prevent unauthorized modifications, and reduce the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access to critical files.
IT admins should enable controlled folder access on Windows devices, define protected folders and whitelist trusted applications, and regularly review and update controlled folder access settings to protect critical data from unauthorized changes or encryption.
Windows 11 provides a range of application security features that work together to protect users from a variety of cyber threats, including malware, phishing attacks, and other forms of malicious software. These features provide users with a secure computing environment, allowing them to use their devices with confidence.
One of these features is Windows Defender Application Control, which helps control the applications that are allowed to run on Windows devices. It uses policies to allow only trusted applications to run, ensuring that malware or other malicious programs cannot execute on the device. IT admins should consider using Windows Defender Application Control to enforce application whitelisting on all Windows devices. This will help prevent malware from executing on the device and provide an additional layer of security.
Another security feature in Windows 11 is Microsoft Defender Application Guard, which provides a secure virtual environment to isolate potentially harmful applications or websites from the rest of the device. The purpose of this feature is to actively prevent malware from accessing sensitive data or causing harm to the device.
Moreover, Application Guard is specifically designed to cater to various types of devices, including domain-joined and organization-managed enterprise desktops and enterprise mobile laptops. IT admins primarily perform configuration management using Microsoft Configuration Manager, Microsoft Intune or any other device management software. In these cases, employees typically hold Standard User privileges and utilize high-bandwidth, wired corporate networks. Additionally, there are bring your own device (BYOD) mobile laptops, which are personally owned but managed by the organization via tools like Microsoft Intune. Users of these laptops are typically admins on the devices and connect to high-bandwidth, wireless corporate networks at work, and comparable personal networks at home. Finally, there are personal devices such as personally owned desktops or mobile laptops that are not domain-joined or managed by any organization. Users of these devices hold admin privileges and connect to high-bandwidth wireless personal networks at home, or comparable public networks when outside.
Windows Sandbox is a Windows 11 security feature that provides a secure, isolated environment to run potentially suspicious applications. It is a lightweight virtual machine that runs a clean, disposable instance of Windows, allowing users to test new software or potentially harmful applications without risking the security of the device. Furthermore, Windows Sandbox uses integrated kernel scheduler and smart memory management techniques to optimize performance and minimize resource usage.
An IT admin can use Windows Sandbox to provide a secure environment for users to browse the web or open suspicious files. By configuring Windows Sandbox to automatically delete any changes made during a session, admins can ensure that any potentially harmful files or websites are completely removed from the system after use.
Microsoft Defender SmartScreen is yet another application security feature in Windows 11 that helps protect against phishing and other online attacks. It provides real-time protection against unsafe websites and downloads by checking URLs against a constantly updated list of known malicious websites. SmartScreen also checks downloaded files and applications against a database of known malicious software, alerting users if a threat is detected.
User security and secured identity are critical aspects of an organization’s overall security posture. Windows provides various features and technologies to enhance user identity protection and access control. IT admins should prioritize user security and secured identity by implementing recommended actions such as enabling Windows Hello, configuring Windows Defender Credential Guard, promoting FIDO2-based authentication, encouraging the use of Microsoft Authenticator, deploying smart card infrastructure, and implementing robust access control mechanisms. These measures enhance user security, mitigate the risks associated with password-based authentication, and protect against unauthorized access.
Windows Hello is a biometric authentication feature that enables users to sign into their devices using facial recognition, fingerprints, or PINs. It provides a secure and convenient way to authenticate user identities, reducing the reliance on passwords. Windows Hello for Business extends this capability to enterprise environments, allowing IT admins to implement strong user authentication practices. Admins should encourage users to set up Windows Hello and enforce its usage to enhance user security and protect against unauthorized access.
These features protect user credentials from theft and unauthorized access. Windows Defender Credential Guard isolates user credentials in a secure environment, preventing credential theft through techniques like pass-the-hash attacks. Remote Credential Guard extends this protection to remote desktop sessions, ensuring that user credentials are never exposed to the remote host. IT admins should enable and configure Credential Guard on devices, particularly for users with elevated privileges or accessing sensitive resources, to prevent credential-based attacks.
Microsoft Authenticator is a mobile app that provides two-factor authentication (2FA) and password-less sign-in options. IT admins can recommend and guide users to leverage Microsoft Authenticator for additional security when accessing corporate resources. To enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) with the Microsoft Authenticator app, users are required to connect the app to their account by either scanning a QR code or entering a provided code. When logging in, users receive a push notification on their mobile device and must confirm the login request within the app. Additionally, the app can generate a one-time code as an alternative authentication method. Furthermore, the app also facilitates password-less authentication using biometrics, making it harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access to user accounts. By leveraging MFA through the Microsoft Authenticator app, users can enhance the security of their accounts and mitigate the risk of unauthorized access.
Smart cards are physical devices that store cryptographic keys and certificates used for authentication. Windows supports smart card-based authentication, allowing users to securely access resources using their smart cards. IT admins can deploy smart card infrastructure within the organization and enforce their usage for highly sensitive operations or privileged accounts.
Access control mechanisms play a crucial role in user security. Windows provides various access control technologies such as Windows Hello, biometric authentication, Group Policy, and Active Directory-based access controls. By implementing authentication and permission protocols, it empowers organizations to exercise full control over their resources, verifying the authenticity of user identities and granting appropriate access to corporate data. This ensures that only authorized personnel or individuals possessing valid credentials can successfully navigate through the system. IT admins should configure access control policies and permissions appropriately, ensuring that users only have access to the resources necessary for their roles. Regular reviews and updates to access control policies help maintain a secure environment and prevent unauthorized access.
The Zero Trust security model is a security approach that assumes that no user or device should be trusted automatically, even if they are within the organization’s network. Instead, Zero Trust requires verification for every access request, regardless of whether the user or device is inside or outside the network perimeter. This approach aims to reduce the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks by enforcing strict access controls and verifying user identities and devices before granting access to resources.
The security features introduced in Windows 11 are specifically designed to enhance protection for hybrid work environments, where employees may be working both remotely and in office settings. These features address the unique challenges and security risks associated with this modern work arrangement. Windows 11 includes advanced identity and access management capabilities, such as Windows Hello and multi-factor authentication, to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data and applications. This helps protect against unauthorized access and identity theft.
Additionally, Windows 11 introduces hardware security enhancements like Microsoft Pluton and TPM, which provide a secure hardware root of trust. These features protect against firmware-level attacks and provide a secure foundation for the operating system. Windows Defender System Guard, another key security component, safeguards devices against firmware-level attacks and helps maintain the integrity of the system. It includes features like Secure Boot and Memory Integrity to ensure that the device is protected against malicious software and unauthorized modifications.
Furthermore, Windows 11 offers robust application security features, such as Windows Defender Application Control and Microsoft Defender SmartScreen, which help protect against malware, phishing attacks, and other threats. These features play a vital role in securing the applications used in hybrid work scenarios, effectively safeguarding users while they access different resources.
So, IT admins must take the initiative to implement these security features, ensuring that devices are correctly configured and regularly updated. For this, they should conduct routine security assessments and monitoring to detect and resolve any vulnerabilities promptly. Additionally, IT admins should educate employees about best practices for secure remote work, including the importance of strong passwords, regular software updates, and being vigilant against social engineering attacks.
A Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) solution can significantly enhance Windows 11 security. By centralizing device management, a UEM provides a comprehensive set of security tools and features. It enables IT admins to enforce strong password policies, manage restrictions, and streamline app management. Additionally, UEM solutions facilitate network configuration, threat management, and remote access capabilities, all essential components of a robust security strategy for Windows 11 devices.
Everything you need to know about the Hexnode Windows UEM app
Managing operating system (OS) updates in an enterprise environment can be a daunting task. However, utilizing scripts can simplify the process and ensure timely updates across Windows devices. By leveraging scripts, IT admins can automate the deployment of OS updates, eliminating the need for manual intervention. This approach allows for seamless scheduling and ensures that critical security patches and feature updates are promptly applied. Furthermore, scripts provide flexibility, enabling organizations to tailor the update process to their specific requirements, such as staging updates, managing dependencies, and handling device reboots effectively. Implementing OS update management through scripts empowers IT teams to maintain a secure and up-to-date Windows environment with minimal effort.
Establishing a robust password policy is paramount in safeguarding Windows devices against unauthorized access. With a comprehensive UEM solution like Hexnode, organizations can enforce stringent password policies for their Windows devices. This includes setting minimum password length, complexity requirements, and password expiration intervals. By implementing a password policy, organizations can mitigate the risk of password-related security breaches. Hexnode UEM offers a wide range of password-related configurations, such as password history restrictions, lockout policies, and account lock thresholds, further enhancing the overall security posture of Windows devices.
To ensure a secure computing environment, organizations need to enforce specific restrictions on Windows devices. Hexnode UEM offers extensive capabilities to manage restrictions effectively. IT administrators can limit access to critical device settings and features, control app installations, and enforce data protection policies. Restrictions can be applied to various areas, including network settings, device functionalities, and system configurations. Furthermore, Hexnode’s flexible restrictions management empowers organizations to customize Windows devices according to specific security and compliance requirements. This enhances data protection and minimizes potential vulnerabilities.
Efficiently managing apps on Windows devices is essential for maintaining security and productivity. With Hexnode’s app distribution and installation capabilities, IT admins can seamlessly deploy applications to Windows devices, ensuring authorized access to necessary tools. Furthermore, Hexnode also enables organizations to update apps, and remove unauthorized or obsolete applications. Additionally, app blacklisting and whitelisting capabilities offer granular control over app usage, preventing the installation of malicious or non-compliant applications on Windows devices.
Configuring Wi-Fi and VPN settings on Windows devices can be simplified and streamlined with the UEM solution. IT administrators can centrally manage and deploy Wi-Fi configurations, ensuring secure and seamless connectivity. Hexnode enables the configuration of Wi-Fi credentials, pre-shared keys, and network authentication settings, while also providing options to prioritize Wi-Fi networks and automatically connect to preferred networks. In addition, Hexnode UEM facilitates the configuration of VPN settings, including VPN protocols, server details, and user authentication credentials. This comprehensive network management approach enables organizations to establish secure connections and optimize network performance on Windows devices.
Microsoft Defender plays a pivotal role in securing Windows devices against a wide range of threats. Integrated within Windows 11, Microsoft Defender offers robust protection against malware, viruses, and other malicious activities. It employs advanced threat detection techniques, including real-time scanning, cloud-based protection, and behavioral analysis. With Microsoft Defender, organizations can safeguard their Windows devices from evolving threats, while also benefiting from features such as firewall management, web protection, and device health monitoring. Hexnode UEM enables administrators to easily configure a range of Microsoft Defender settings on devices that are enrolled in the portal.
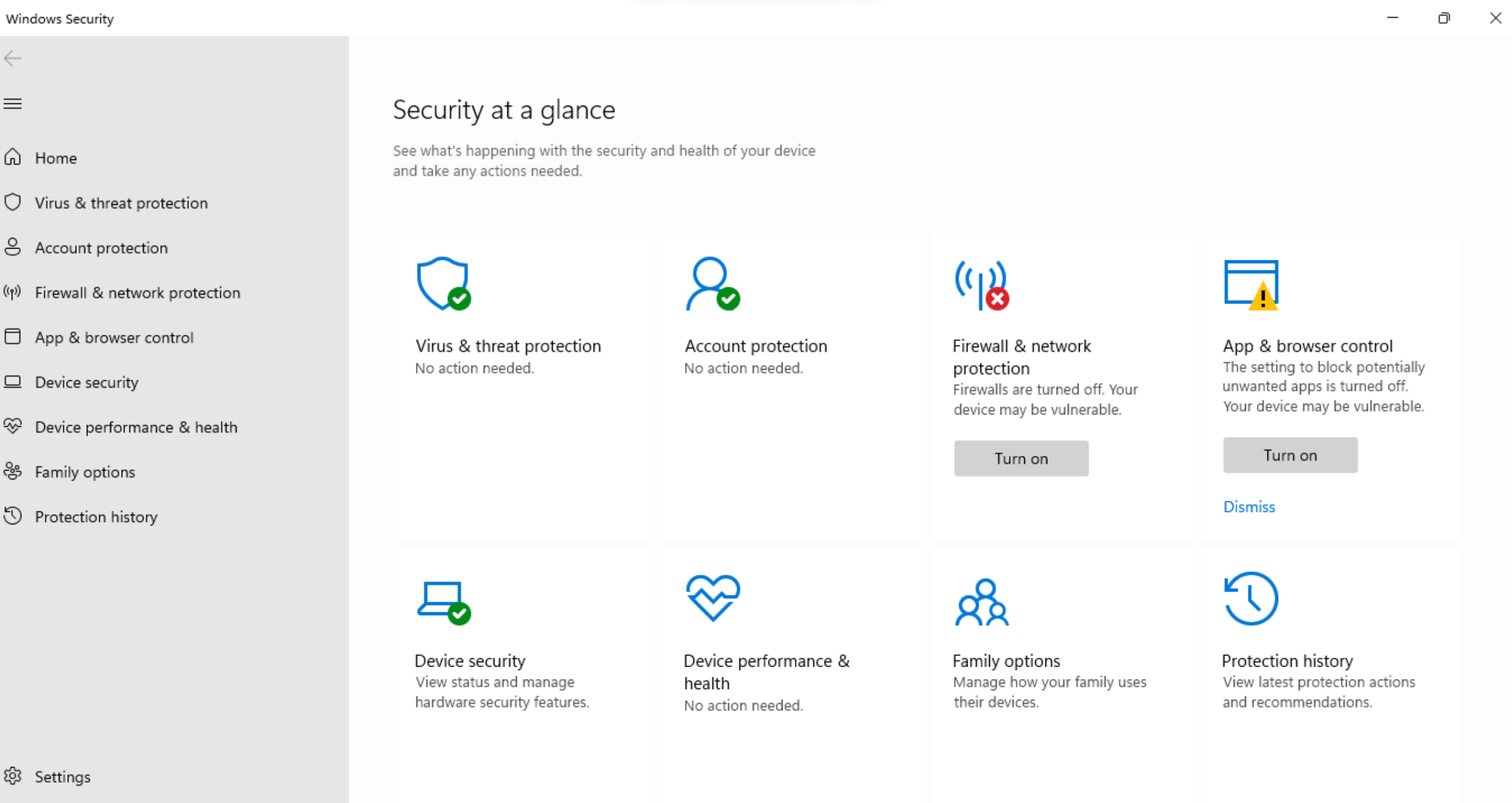
BitLocker, a full-disk encryption feature, is a powerful tool for safeguarding sensitive data. By encrypting entire drives, BitLocker ensures that even if a device is lost or stolen, the data remains inaccessible to unauthorized users. It provides strong encryption algorithms and secure key management, protecting data at rest. BitLocker also integrates with other security features, such as Secure Boot and TPM, further enhancing the overall security posture of Windows devices. Deploying and managing BitLocker across an organization can be simplified with Hexnode UEM, offering centralized control and monitoring of encryption policies and recovery keys.
Enabling remote access to Windows devices is essential for modern work environments, facilitating flexibility and productivity. Hexnode UEM provides robust remote access capabilities for Windows devices, empowering IT teams to manage devices and troubleshoot issues remotely. With remote control functionality, IT admins can securely access and control Windows devices from anywhere, addressing technical problems and performing necessary configurations. Hexnode also offers remote view and file transfer features, allowing efficient collaboration and support.
Windows 11 introduces significant security enhancements that prioritize user privacy and protect against cyber threats. The integration of features such as TPM 2.0, secure boot, Windows Hello, Microsoft Defender Antivirus, and improved Windows Firewall establishes a strong foundation for safeguarding user data and preventing unauthorized access. While no operating system is impervious to risks, Windows 11, combined with responsible user practices, creates a more secure computing environment. By staying informed and leveraging the advanced Windows 11 security features offered, users and IT admins can mitigate potential threats and enjoy a safer digital experience.
Give Hexnode UEM a go to effectively manage and secure all your Windows devices.
Start your free trial
Share your thoughts